In-cluster Git Server
In-cluster Git Server
Overview
Starting with the patterns operator version 0.0.52 there is an initial (experimental) support for having an in-cluster git server. Once enabled, a very simple gitea server is installed and configured inside the cluster. The patterns will use the internal gitea server to pull code from. By default the Gitea server repository will sync from the upstream git repo every eight hours.
Why
One of the main reasons to have an in-cluster git server is to make it simpler to get started with patterns. It avoids the need to have a fork of the original pattern’s git repo and the changes can be done directly in the in-cluster git repository.
How to get started
There are fundamentally two ways to set up the in-cluster gitea server.
- Via the user interface in the console by enabling the
In Cluster Git Serverswitch inside theGit Configsection: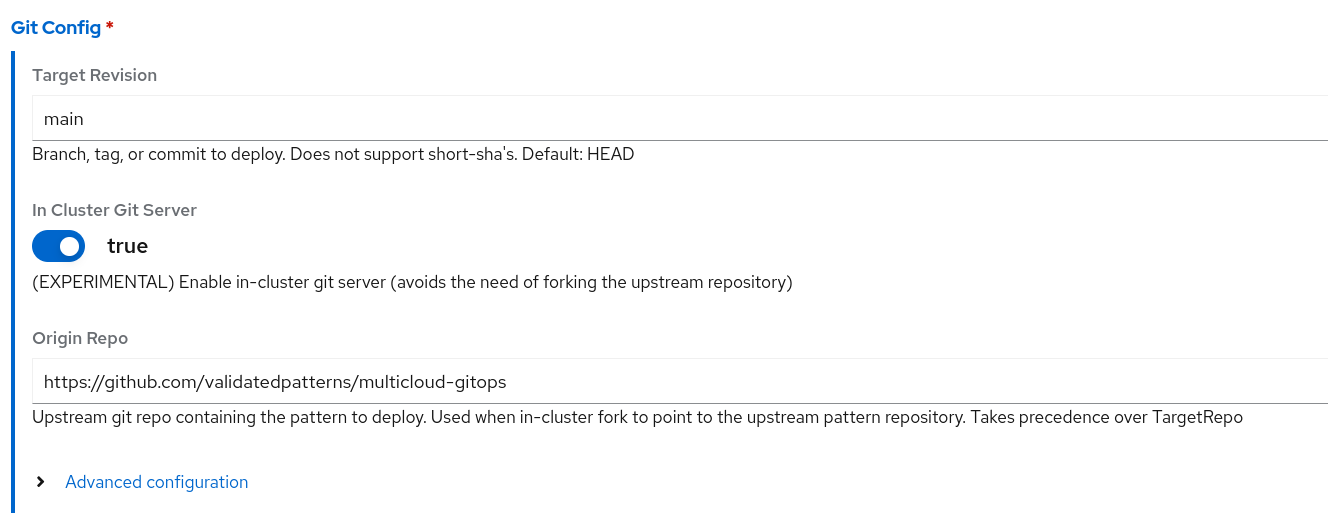 And setting the
And setting the Origin Repoto the upstream git repository that needs to be imported in gitea. - By creating a Pattern CR and setting the
spec.gitSpec.originRepofield to the upstream git repository. In this case thespec.gitSpec.targetRepofield, which is used by the pattern to deploy the actual code, will be automatically overwritten pointing to the internal in-cluster git route. For example:In the example above, sinceapiVersion: gitops.hybrid-cloud-patterns.io/v1alpha1 kind: Pattern metadata: name: test-pattern namespace: openshift-operators spec: clusterGroupName: hub gitSpec: originRepo: https://github.com/validatedpatterns/multicloud-gitops targetRevision: mainoriginRepois not empty it will be used as the upstream git repository to clone from and that repository will be imported into gitea andtargetRepowill be automatically constructed to point to the internal gitea.
Configuration
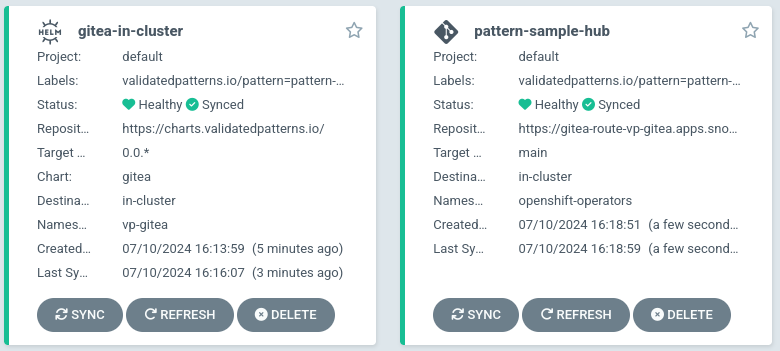
Once the in-cluster gitea is enabled, its configuration will be done via a normal argo application
that can be seen in the cluster-wide argo:
The gitea interface can be accessed via the gitea-route inside the vp-gitea namespace or by clicking
the console link on the nine box:
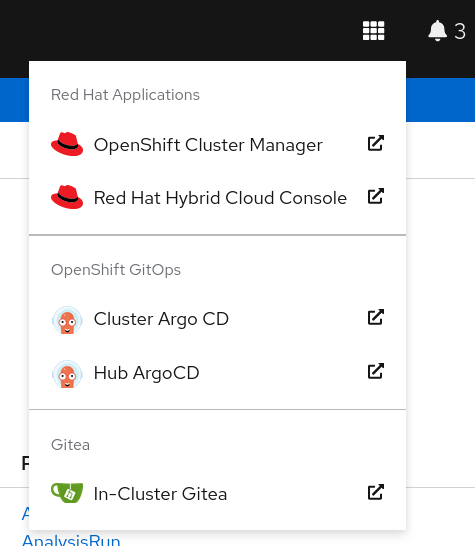
To access the gitea admin interface a secret called gitea-admin-secret
containing username and password are created inside the vp-gitea namespace.
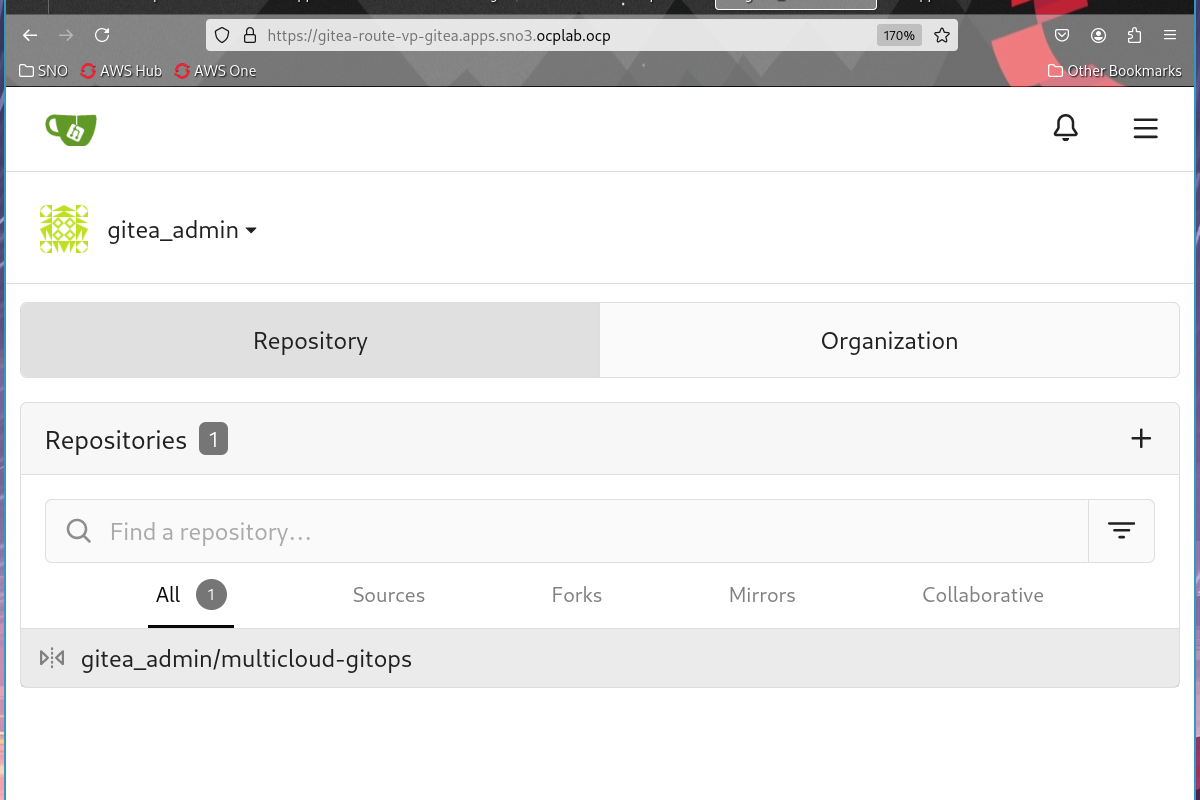
Repositories
Once logged in with the gitea_admin user whose password is contained in the gitea-admin-secret
you will see the repository that has been configured inside gitea:
Clicking on the repository will show the actual code and the usual git related information (branch, tags, etc):
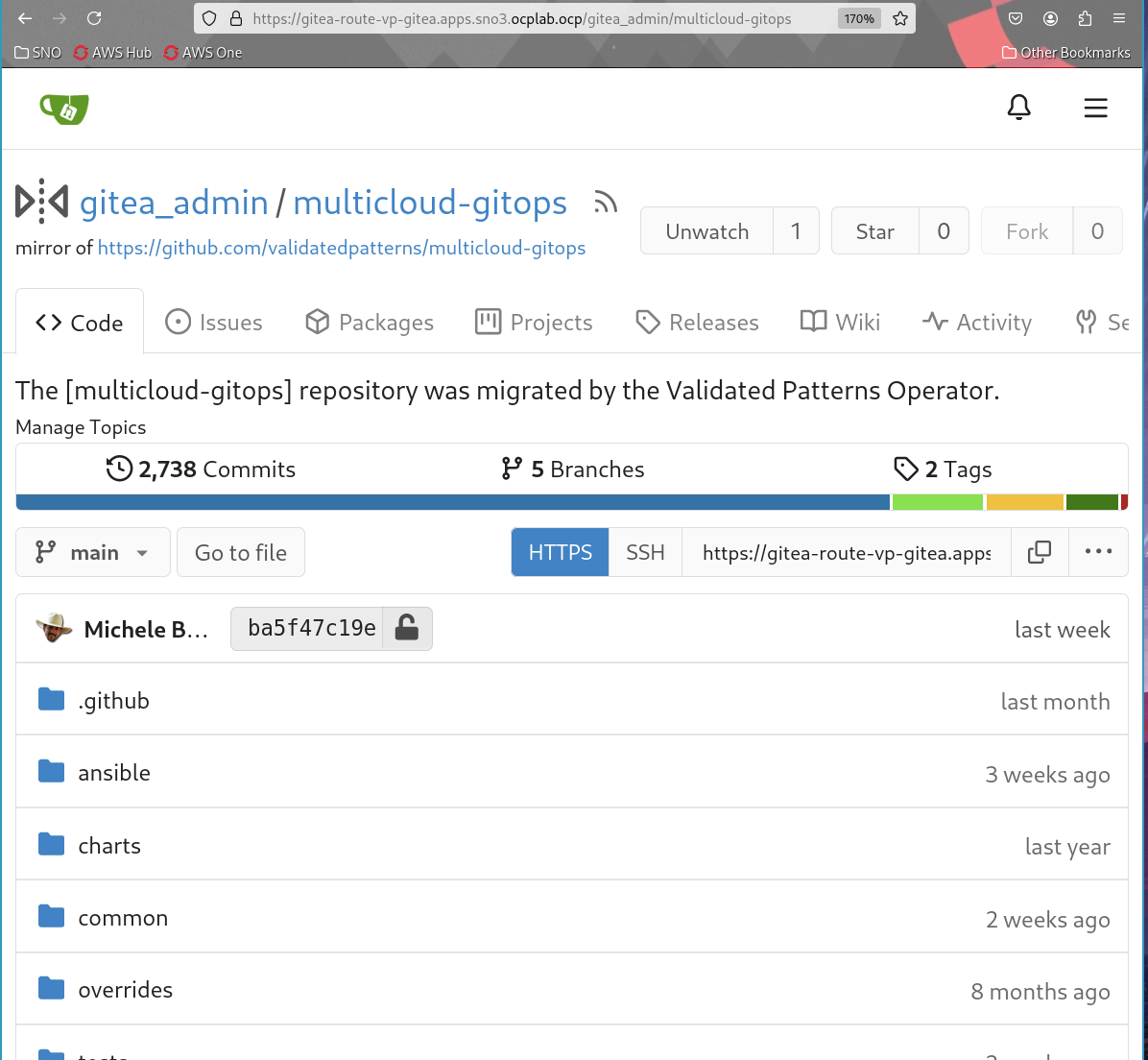
Gitea usage
To clone the gitea repository you can simply clone the repository via https:
git -c http.sslVerify=false clone https://gitea-route-vp-gitea.apps.mcg-hub.aws.validatedpatterns.io/gitea_admin/multicloud-gitops.git
In order to avoid the sslVerify=false setting you need to download your clusters CA and import it into the git config.
You can create a token in gitea under Settings -> Applications -> Manage Access Tokens that repository Read and Write permissions. With this token
you can clone it once with authentication and then push changes to the gitea
repository:
git -c http.sslVerify=false clone https://gitea_admin:<token>@gitea-route-vp-gitea.apps.mcg-hub.aws.validatedpatterns.io/gitea_admin/multicloud-gitops.git
git -c http.sslVerify=false push origin mytestbranch
Note: The conversion from gitea mirror to regular repository is needed unless the upstream issue gets implemented.
