$ git clone git@github.com:your-username/ansible-edge-gitops.gitDeploying the Ansible Edge GitOps pattern
An OpenShift cluster
To create an OpenShift cluster, go to the Red Hat Hybrid Cloud console.
Select OpenShift -> Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform -> Create cluster.
A GitHub account with a personal access token that has repository read and write permissions.
The Helm binary, for instructions, see Installing Helm
Additional installation tool dependencies. For details, see Patterns quick start.
It is desirable to have a cluster for deploying the GitOps management hub assets and a separate cluster(s) for the managed cluster(s).
Preparing for deployment
Fork the ansible-edge-gitops repository on GitHub. You must fork the repository because your fork is updated as part of the GitOps and DevOps processes.
Clone the forked copy of this repository.
Go to your repository: Ensure you are in the root directory of your Git repository by using:
$ cd /path/to/your/repositoryRun the following command to set the upstream repository:
$ git remote add -f upstream git@github.com:validatedpatterns/ansible-edge-gitops.gitVerify the setup of your remote repositories by running the following command:
$ git remote -vExample outputorigin git@github.com:kquinn1204/ansible-edge-gitops.git (fetch) origin git@github.com:kquinn1204/ansible-edge-gitops.git (push) upstream git@github.com:validatedpatterns/ansible-edge-gitops.git (fetch) upstream git@github.com:validatedpatterns/ansible-edge-gitops.git (push)Make a local copy of secrets template outside of your repository to hold credentials for the pattern.
Do not add, commit, or push this file to your repository. Doing so may expose personal credentials to GitHub.
Run the following commands:
$ cp values-secret.yaml.template ~/values-secret.yamlPopulate this file with secrets, or credentials, that are needed to deploy the pattern successfully:
$ vi ~/values-secret.yamlEdit the
vm-sshsection to include the username, private key, and public key. To ensure the seamless flow of the pattern, the value associated with theprivatekeyandpublickeyhas been updated withpath. For example:- name: vm-ssh fields: - name: username value: 'cloud-user' - name: privatekey path: '/path/to/private-ssh-key' - name: publickey path: '/path/to/public-ssh-key'Paste the path to your locally stored private and public keys. If you do not have a key pair, generate one using
ssh-keygen.Edit the
rhsmsection to include the Red Hat Subscription Management username and password. For example:- name: rhsm fields: - name: username value: 'username of user to register RHEL VMs' - name: password value: 'password of rhsm user in plaintext'This is the username and password that you use to log in to registry.redhat.io..
Edit the
kiosk-extrasection and populate as shown below:- name: kiosk-extra fields: # Default: '--privileged -e GATEWAY_ADMIN_PASSWORD=redhat' - name: container_extra_params value: '--privileged -e GATEWAY_ADMIN_PASSWORD=redhat'Edit the
cloud-initsection to include theuserDatablock to use with cloud-init. For example:- name: cloud-init fields: - name: userData value: |- #cloud-config user: 'cloud-user' password: 'cloud-user' chpasswd: { expire: False }Edit the
aap-manifestsection to include the path to the downloaded manifest zip file that gives an entitlement to run Ansible Automation Platform. Create a subscription manifest by following the guidance at Obtaining a manifest file. For example add the following:- name: aap-manifest fields: - name: path: '~/Downloads/<manifest_filename>.zip' base64: trueEdit the
automation-hub-tokensection to include the token generated at the Load token link at Automation Hub Token to generate a token. For example:- name: automation-hub-token fields: - name: token path: '/path/to/automation-hub-token'Optionally: Edit the
agof-vault-filesection to use the following (you do not need additional secrets for this pattern):- name: agof-vault-file fields: - name: agof-vault-file value: '---' base64: true
Create and switch to a new branch named
my-branch, by running the following command:$ git checkout -b my-branchEdit the
values-global.yamlfile to customize the deployment for your cluster. The defaults invalues-global.yamlare designed to work in AWS. For example:$ vi values-global.yamlAdd the changes to the staging area by running the following command:
$ git add values-global.yamlCommit the changes by running the following command:
$ git commit -m "any updates"Push the changes to your forked repository:
$ git push origin my-branch
The preferred way to install this pattern is by using the script ./pattern.sh script.
Deploying the pattern by using the pattern.sh file
To deploy the pattern by using the pattern.sh file, complete the following steps:
Log in to your cluster by following this procedure:
Obtain an API token by visiting https://oauth-openshift.apps.<your-cluster>.<domain>/oauth/token/request.
Log in to the cluster by running the following command:
$ oc login --token=<retrieved-token> --server=https://api.<your-cluster>.<domain>:6443Or log in by running the following command:
$ export KUBECONFIG=~/<path_to_kubeconfig>
Deploy the pattern to your cluster. Run the following command:
$ ./pattern.sh make install
Verify that the Operators have been installed. Navigate to Operators → Installed Operators page in the OpenShift Container Platform web console,
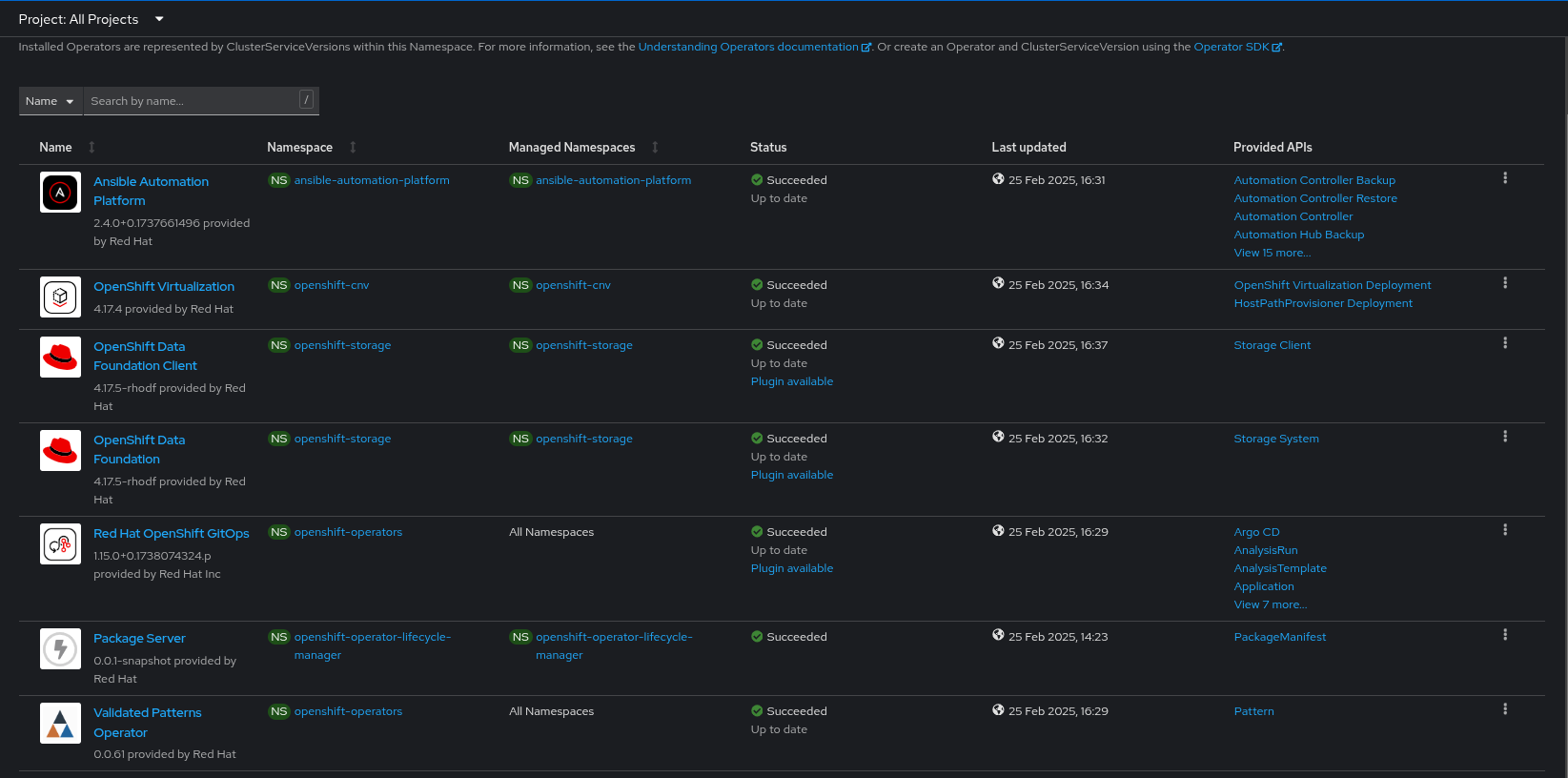 Figure 1. Ansible Edge GitOps Operators
Figure 1. Ansible Edge GitOps OperatorsWait some time for everything to deploy. You can track the progress through the
Hub ArgoCDUI from the nines menu.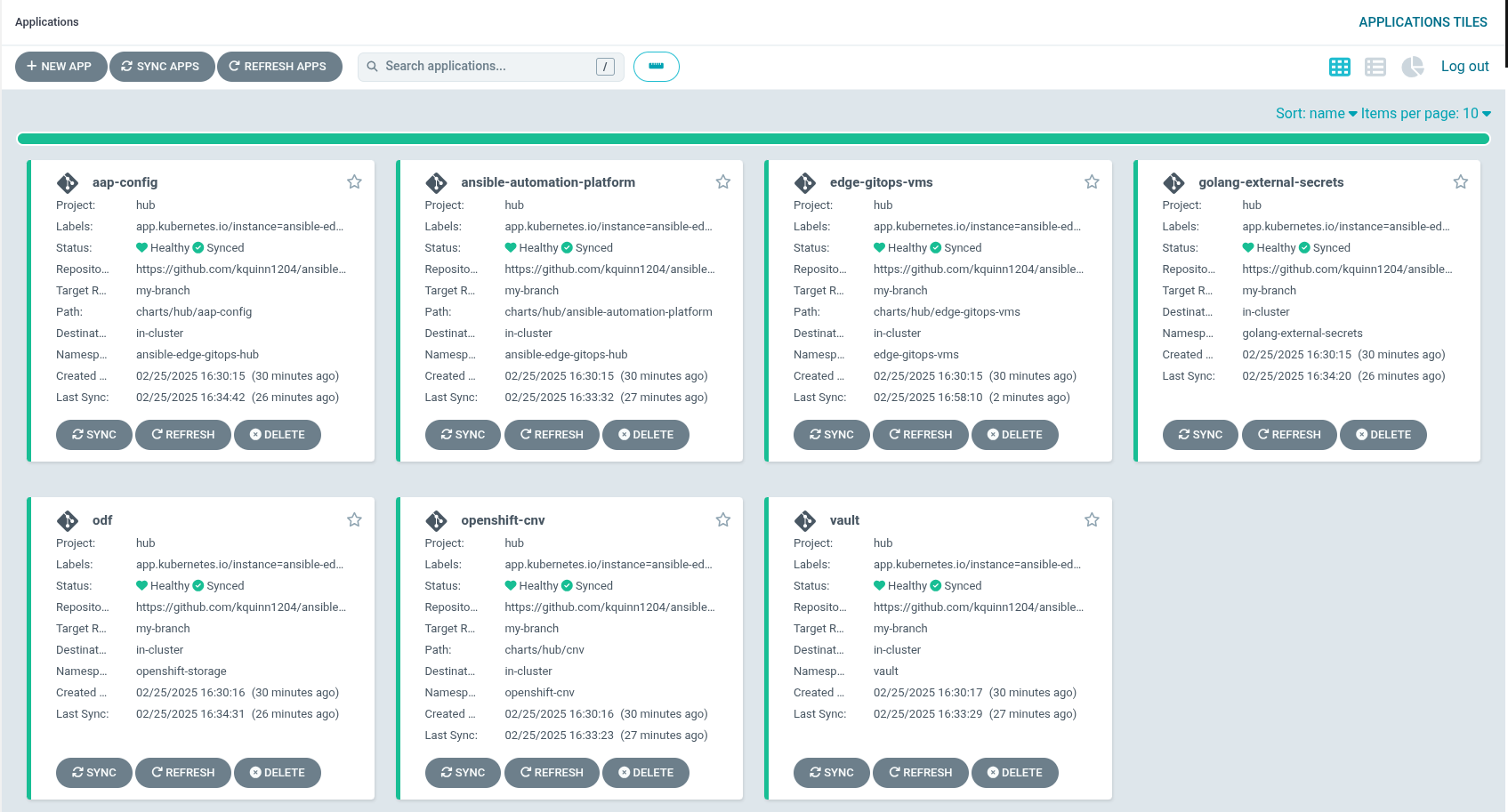 Figure 2. Ansible Edge GitOps Applications
Figure 2. Ansible Edge GitOps Applications
As part of installing by using the script pattern.sh pattern, HashiCorp Vault is installed. Running ./pattern.sh make install also calls the load-secrets makefile target. This load-secrets target looks for a YAML file describing the secrets to be loaded into vault and in case it cannot find one it will use the values-secret.yaml.template file in the git repository to try to generate random secrets.
For more information, see section on Vault.
Under Virtualization > VirtualMachines, the virtual machines show as
Running. Once they are in theRunningstate the provisioning workflow runs on them, and installs Firefox, Kiosk mode, and the Ignition application on them:Select one of the VMs to see the details of the VM. The VMs are named
rhel8-kiosk-001andrhel8-kiosk-002Open the Console tab. Choose any of these options; this section assumes you chose
Ignition - Standard Edition:Read and accept the license agreement and click Finish setup.
Click Start Gateway to start the Ignition Gateway.
Log in to the application with the userid
adminand the password you specified as the GATEWAY_ADMIN_PASSWORD incontainer_extra_paramsin yourvalues-secret.yamlfile.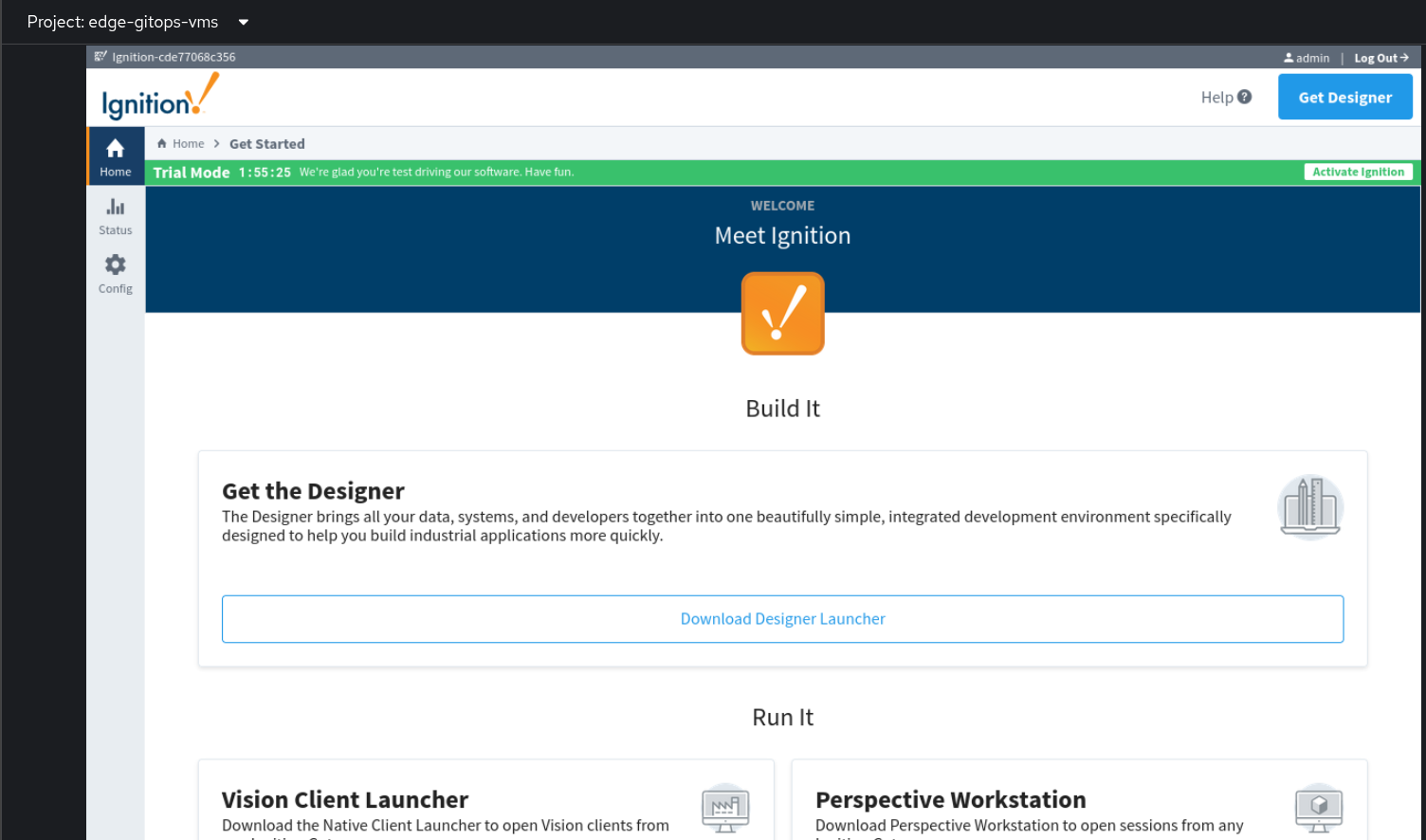 Figure 3. Ansible Edge GitOps VM Console
Figure 3. Ansible Edge GitOps VM ConsoleSee Installation Details for more information about the installation steps.
See Ansible Automation Platform for more information about how this pattern uses the Ansible Automation Platform Operator for OpenShift.
See OpenShift Virtualization for more information about how this pattern uses OpenShift Virtualization.
Infrastructure Elements of this Pattern
Ansible Automation Platform
A fully functional installation of the Ansible Automation Platform operator is installed on your OpenShift cluster to configure and maintain the VMs for this demo. AAP maintains a dynamic inventory of kiosk machines and can configure a VM from template to fully functional kiosk in about 10 minutes.
OpenShift Virtualization
OpenShift Virtualization is a Kubernetes-native way to run virtual machine workloads. It is used in this pattern to host VMs simulating an edge environment; the chart that configures the VMs is designed to be flexible to allow easy customization to model different VM sizes, mixes, versions and profiles for future pattern development.
Infrastructure Elements of this Pattern
Ansible Automation Platform
A fully functional installation of the Ansible Automation Platform operator is installed on your OpenShift cluster to configure and maintain the VMs for this demo. AAP maintains a dynamic inventory of kiosk machines and can configure a VM from template to fully functional kiosk in about 10 minutes.
OpenShift Virtualization
OpenShift Virtualization is a Kubernetes-native way to run virtual machine workloads. It is used in this pattern to host VMs simulating an edge environment; the chart that configures the VMs is designed to be flexible to allow easy customization to model different VM sizes, mixes, versions and profiles for future pattern development.
Inductive Automation Ignition
The goal of this pattern is to configure 2 VMs running Firefox in Kiosk mode displaying the demo version of the Ignition application running in a podman container. Ignition is a popular tool in use with Oil and Gas companies; it is included as a real-world example and as an item to spark imagination about what other applications could be installed and managed this way.
The container used for this pattern is the container image published by Inductive Automation.
