Multicluster DevSecOps
Multicluster DevSecOps
Background
With this Pattern, we demonstrate a horizontal solution for multicluster DevSecOps use cases.
It is derived from the multi-cloud GitOps pattern with added products to provide a complete DevSecOps workflow. This includes CI/CD pipelines with security gates; image scanning, signing and storage in a secure registry; deployment to secured clusters that provide advanced security monitoring and alerting.
Solution elements
- How to use a GitOps approach to keep in control of configuration and operations
- How to centrally manage multiple clusters, including workloads
- How to build and deploy workloads across clusters using modern CI/CD
- How to deploy different security products into the pattern
Red Hat Products
- Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform (Kubernetes)
- Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management (Open Cluster Management)
- Red Hat OpenShift GitOps (ArgoCD)
- Red Hat OpenShift Pipelines (Tekton)
- Red Hat Quay (container image registry with security features enabled)
- Red Hat Open Data Foundation (highly available storage)
- Red Hat Advanced Cluster Security (scanning and monitoring)
Other technologies and products
- Hashicorp Vault community edition (secrets management)
Context on Multicluster DevSecOps
Effective cloud native DevSecOps is about securing both the platform and the applications deployed to the platform. Securing the applications deployed is also about securing the supply chain. Not all applications are built in-house. Confidence in external applications and technologies is critical. OpenShift Platform Plus enables DevSecOps for both platform and supply chain.
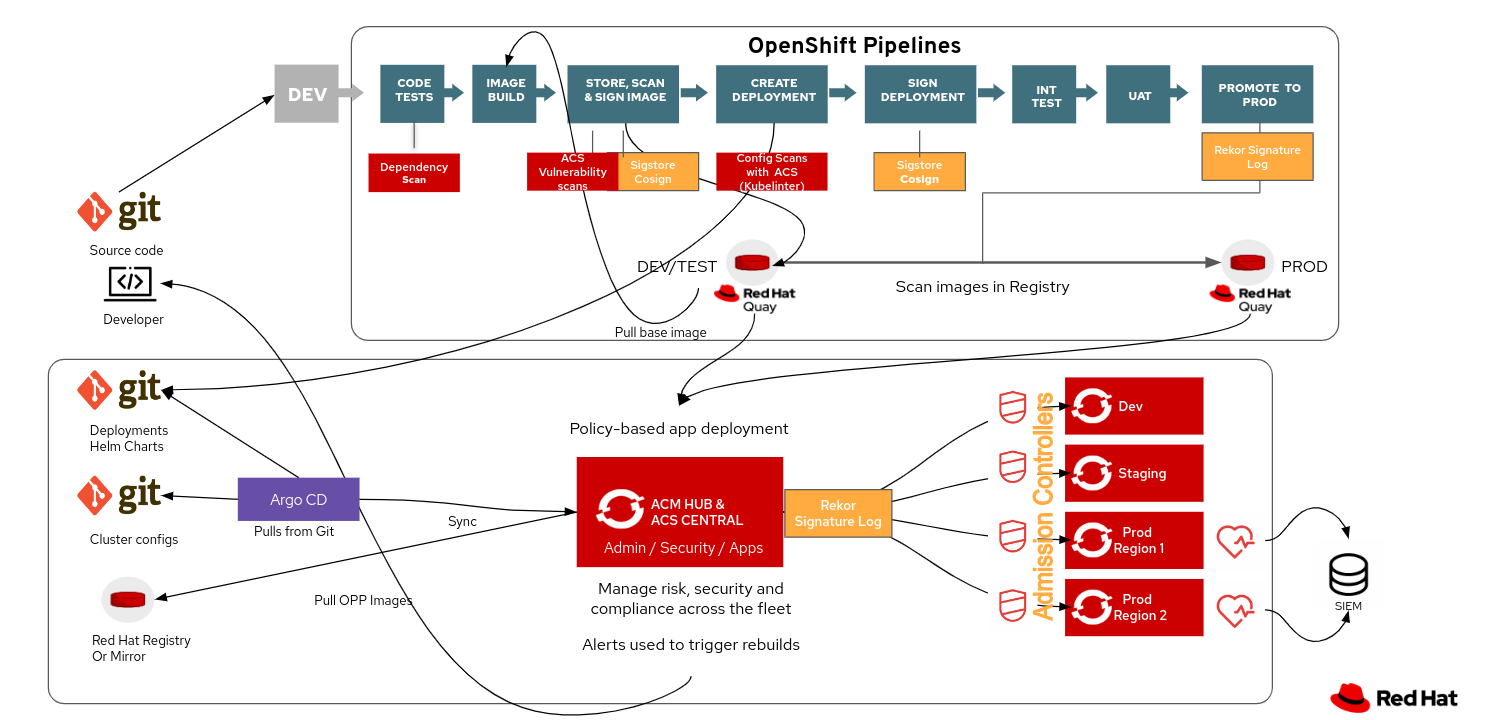
OpenShift Platform Plus includes OpenShift Container Platform, Advanced Cluster Management, Advanced Cluster Security, OpenShift Data Foundation and Red Hat Quay. The capabilities delivered across these components combine to provide policy-based cluster lifecycle management and policy based risk and security management across your fleet of clusters. You can see the flow at the bottom of this graphic.
The Hub cluster is where lifecycle, deployment, security, compliance and risk management policies are defined and is the central management point across clusters. DevSecOps for the platform includes pulling images from Red Hat’s registry, pulling day two configuration code from Git via our integration with ArgoCD, and ensuring that all optional operators are deployed and configured.
Policy based deployment also specifies which admission controllers should be deployed to which clusters, including the ACS admission controller. The Hub also provides a unified view of health, security, risk and compliance across your fleet. We have many of these capabilities in place today, however, they each have their own UI. Over the next few releases, we will be working to provide an integrated multi-cluster user experience for admin, security and developer persona in the OpenShift Console.
Demo Scenario
The Multicluster DevSecOps Pattern / Demo Scenario reflects this by having 3 layers:
- Managed/Secured edge - the edge or production a more controlled environment.
- Devel - where AppDev, Testing etc. is happening
- Central Data Center / Hub - the cloud/core, (and ERP systems of course, not part of the demo).
There are ways of combing these three clusters into a two cluster (hub/devel and secured/edge) and single cluster (all in one). The documentation provides instructions (TBD Link).
Pattern Logical Architecture
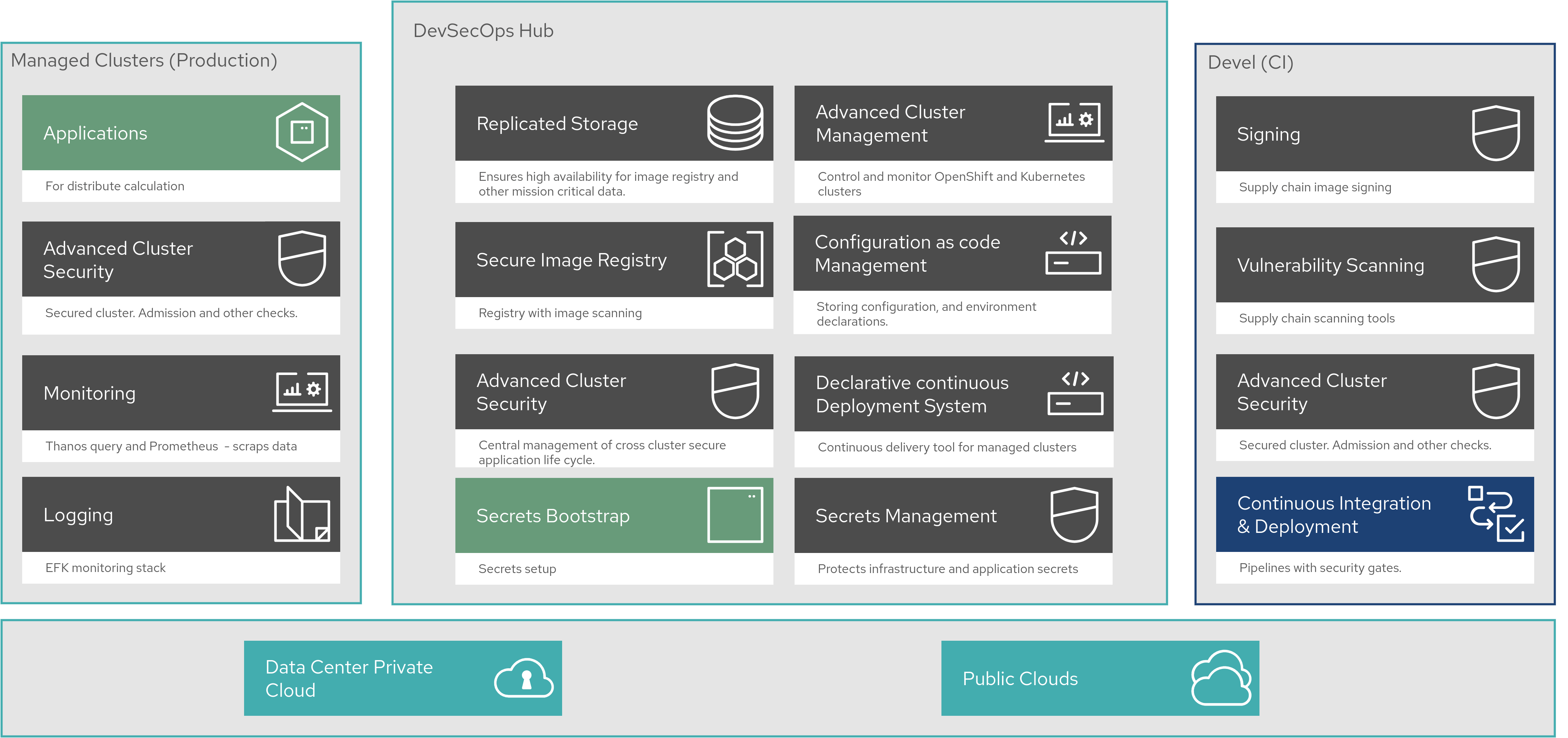
The following diagram explains how different roles have different concerns and focus when working with this distributed AL/ML architecture.
In the Multi-Cluster DevSecOps architecture there are three logical types of sites.
- The Hub. This is where the cloud native infrastructure is monitored and managed. It performs cluster management, advanced cluster security and a secure image registry.
- Devel. This is where the development pipeline is hosted. Developers submit code builds to the pipeline and various security tools are used in the pipeline to mitigate the risk of harmful applications or code being deployed in production.
- Secured Production. This is where applications are securely deployed and monitored.
Pattern Architecture Schema
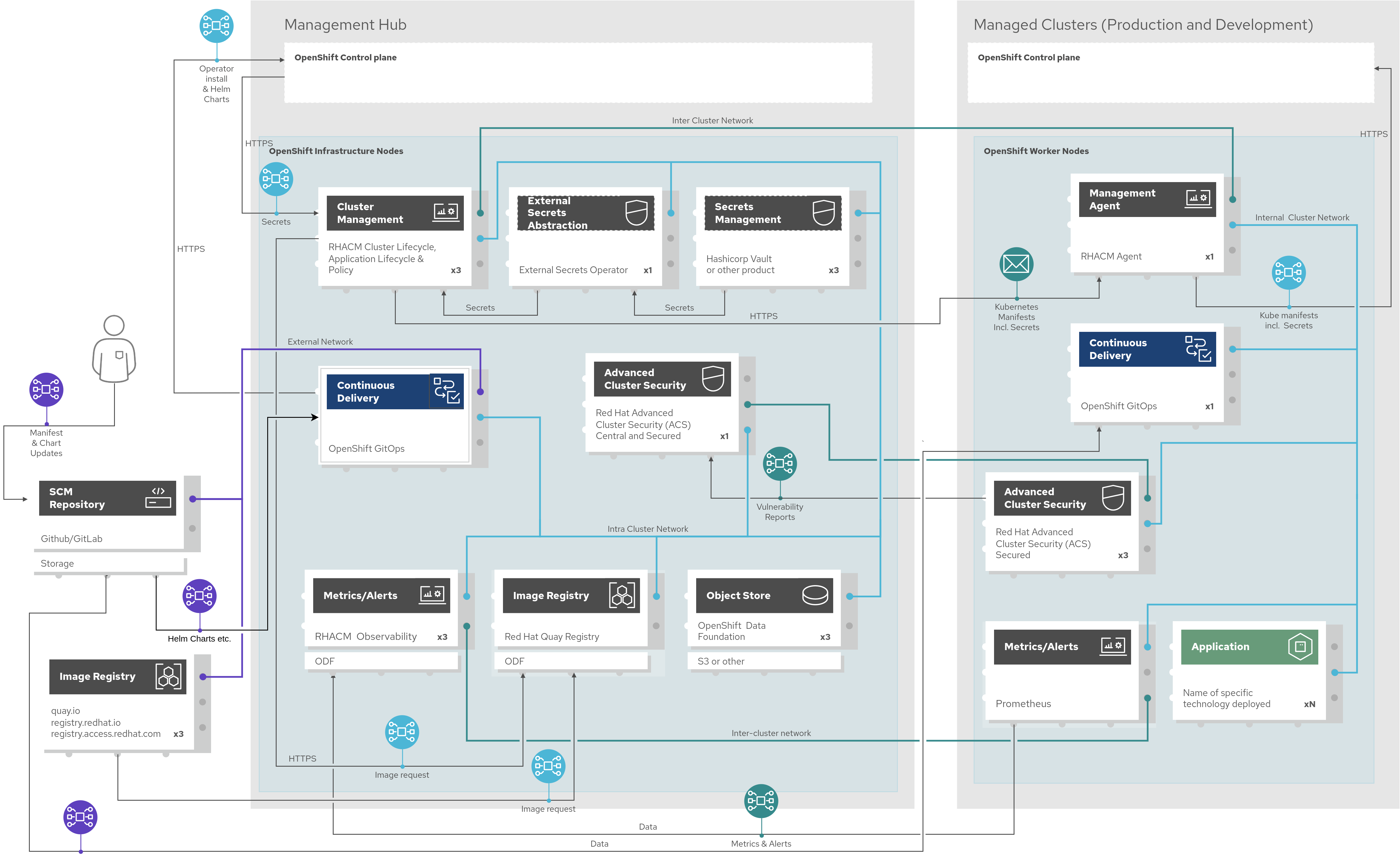
The following diagram shows various management functions, including products and components, that are deployed on central hub and managed clusters (Devel. and Prod.) in order to maintain secure clusters. Consider this the GitOps schema.
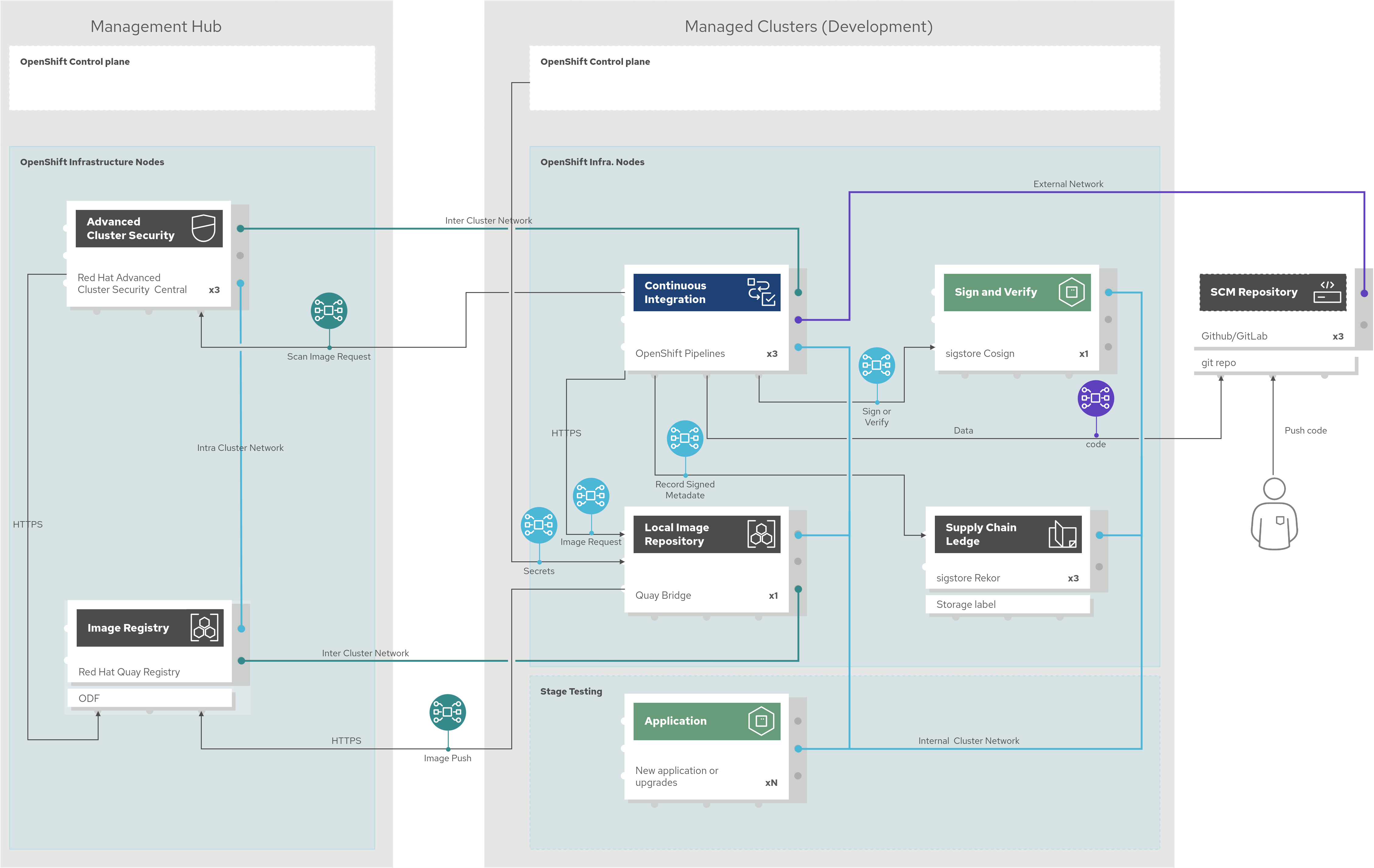
The following diagram shows various development pipeline functions, including products and components, that are deployed on the central hub and development (Devel) clusters in order to provide security features and services for development pipelines. Consider this the DevSecOps schema.