OPEA QnA chat accelerated with Intel Gaudi
Validation status:
Links:
About OPEA QnA chat accelerated with Intel Gaudi pattern
- Background
Validated pattern is based on OPEA [Open Platform for Enterprise AI] example - Chat QnA. OPEA is an ecosystem orchestration framework to integrate performant GenAI technologies & workflows leading to quicker GenAI adoption and business value. Another purpose of this pattern is to deploy whole infrastructure stack enabling Intel Gaudi accelerator. Accelerator is used in the AI inferencing process. Pattern makes use of GitOps approach. GitOps uses Git repositories as a single source of truth to deliver infrastructure-as-code. Submitted code will be checked by the continuous integration (CI) process, while the continuous delivery (CD) process checks and applies requirements for things like security, infrastructure-as-code, or any other boundaries set for the application framework. All changes to code are tracked, making updates easy while also providing version control should a rollback be needed.
- Components
Kernel Module Management operator (KMM) and HabanaAI operator are responsible for providing Gaudi accelerators within the OpenShift cluster, including drivers and monitoring metrics
Node Feature Discovery operator labels all cluster nodes with Gaudi resources available
AI Chat microservices:
Embedding service - is designed to efficiently convert textual strings into vectorized embeddings, facilitating seamless integration into various machine learning and data processing workflows.
Vector Database - stores embedded vectors.
Retriever service - is a highly efficient search service designed for handling and retrieving embedding vectors.
Reranking service - when provided with a query and a collection of documents, reranking swiftly indexes the documents based on their semantic relevance to the query, arranging them from most to least pertinent.
Data preparation service - aims to preprocess the data from various sources (either structured or unstructured data) to text data, and convert the text data to embedding vectors then store them in the database.
LLM service - processes input consisting of a query string and associated reranked documents. It constructs a prompt based on the query and documents, which is then used to perform inference with a large language model.
Backend service
Frontend service
TGI (Text Generation Inference) using Red Hat OpenShift AI
About the solution
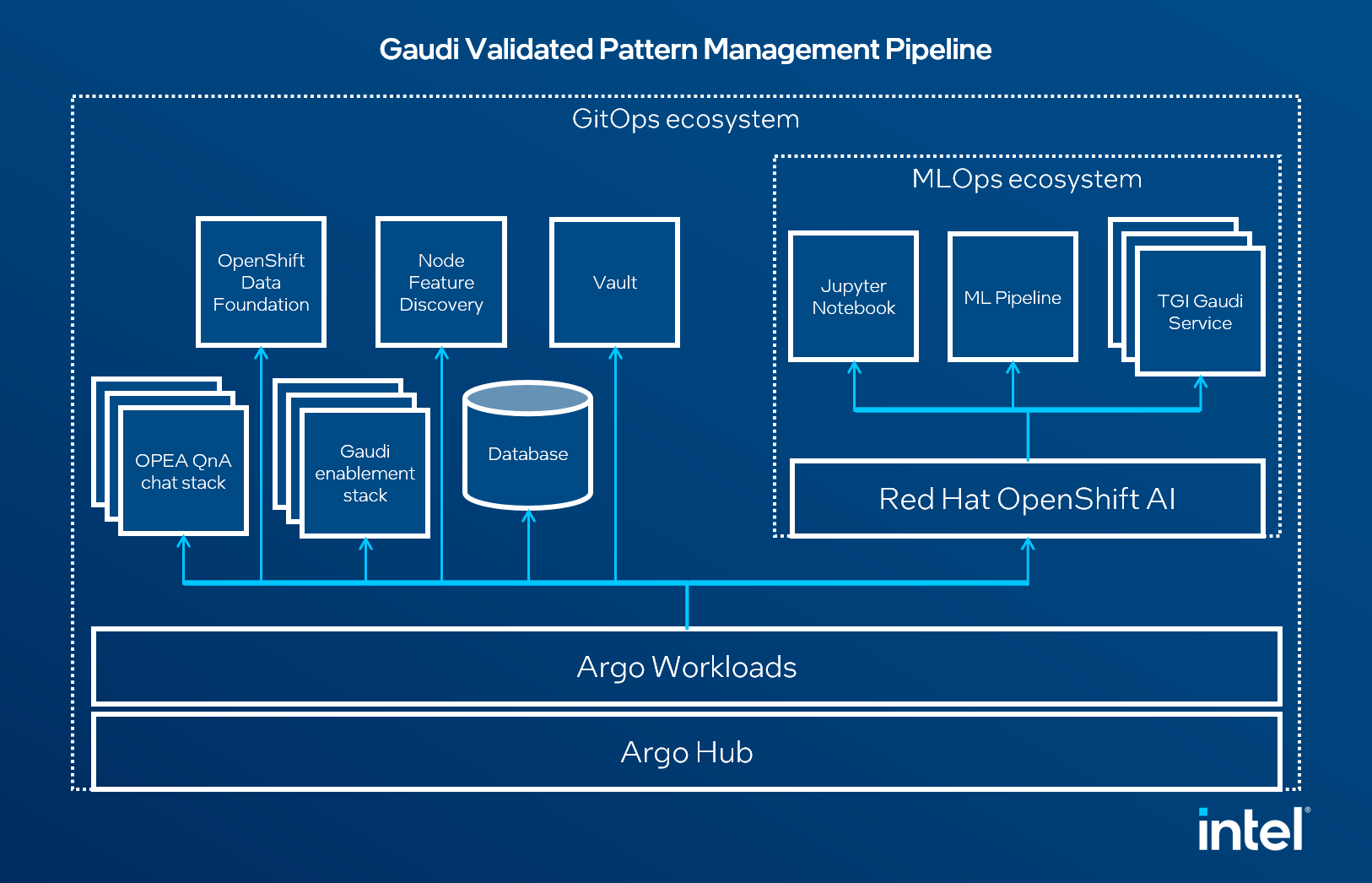
Following solution is based on OPEA [Open Platform for Enterprise AI] example - Chat QnA, but it is additionally wrapped in the Validated Patterns framework. It means that it uses GitOps approach, where every defined component is a microservice and its status can be easily tracked using ArgoCD dashboard. Moreover this approach makes use of OpenShift Data Foundation solution to store all data, like machine learning model on the cluster. AI model in this case is Llama-2-70b-chat-hf. High-level structure of Validated Pattern is shown below:

Figure 1. Overview of the solution
OPEA QnA Chat stack is composed out of Embedding service, Vector Database, Retriever, Reranking service, data preparation service, LLM server and back-/frontend applications.
Gaudi enablement stack consists of Kernel Module Management and HabanaAI operators.
Additionally, in this Validated Pattern OpenShift Data Foundation is used to provide an S3-like storage through Ceph RGW, and Image Registry is used to store all built images and Hashicorp Vault to safely keep HuggingFace User token.
Node Feature Discovery labels Gaudi 2 nodes so the workload can be placed on the right node and benefit from the acceleration.
About the technology
The following technologies are used in this solution:
- Red Hat OpenShift Platform
An enterprise-ready Kubernetes container platform built for an open hybrid cloud strategy. It provides a consistent application platform to manage hybrid cloud, public cloud, and edge deployments. It delivers a complete application platform for both traditional and cloud-native applications, allowing them to run anywhere. OpenShift has a pre-configured, pre-installed, and self-updating monitoring stack that provides monitoring for core platform components. It also enables the use of external secret management systems, for example, HashiCorp Vault in this case, to securely add secrets into the OpenShift platform.
- Red Hat OpenShift GitOps
A declarative application continuous delivery tool for Kubernetes based on the ArgoCD project. Application definitions, configurations, and environments are declarative and version controlled in Git. It can automatically push the desired application state into a cluster, quickly find out if the application state is in sync with the desired state, and manage applications in multi-cluster environments.
- Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform
Provides an enterprise framework for building and operating IT automation at scale across hybrid clouds including edge deployments. It enables users across an organization to create, share, and manage automation, from development and operations to security and network teams.
- Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation
It is software-defined storage for containers. Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation helps teams develop and deploy applications quickly and efficiently across clouds.
- Red Hat OpenShift AI
Red Hat® OpenShift® AI is a flexible, scalable artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) platform that enables enterprises to create and deliver AI-enabled applications at scale across hybrid cloud environments.
- Red Hat OpenShift Serverless
Red Hat® OpenShift® Serverless simplifies the development of hybrid cloud applications by eliminating the complexities associated with Kubernetes and the infrastructure applications are developed and deployed on. Developers will be able to focus on coding applications instead of managing intricate infrastructure details.
- Red Hat OpenShift Service Mesh
Red Hat® OpenShift® Service Mesh provides a uniform way to connect, manage, and observe microservices-based applications. It provides behavioral insight into—and control of—the networked microservices in your service mesh.
- Hashicorp Vault
Provides a secure centralized store for dynamic infrastructure and applications across clusters, including over low-trust networks between clouds and data centers.
- OPEA
OPEA is an ecosystem orchestration framework to integrate performant GenAI technologies & workflows leading to quicker GenAI adoption and business value.
