Deploying the Industrial Edge Pattern
Prerequisites
An OpenShift cluster
To create an OpenShift cluster, go to the Red Hat Hybrid Cloud console.
Select OpenShift → Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform → Create cluster.
The cluster must have a dynamic
StorageClassto provisionPersistentVolumes. Verify that a dynamicStorageClassexists before creating one by running the following command:oc get storageclass -o custom-columns=NAME:.metadata.name,PROVISIONER:.provisioner,DEFAULT:.metadata.annotations."storageclass\.kubernetes\.io/is-default-class"Example output:
NAME PROVISIONER DEFAULT gp2-csi ebs.csi.aws.com <none> gp3-csi ebs.csi.aws.com trueFor more information about creating a dynamic
StorageClass, see the Dynamic provisioning documentation.
Optional: A second OpenShift cluster for the edge/factory.
The use of this pattern depends on having at least one running Red Hat OpenShift cluster. However, consider creating a cluster for deploying the GitOps management hub assets and a separate cluster for the managed cluster.
For installation tooling dependencies, see Patterns quick start
The Industrial Edge pattern installs an in-cluster gitea instance by default. This means that there is no need to fork the pattern’s git repository and that ArgoCD will point directly at the in-cluster git repository. Changes should be done there and not on github. See this post for more information.
Procedure
Clone the industrial-edge repository on GitHub by running the following command:
$ git clone git@github.com:validatedpatterns/industrial-edge.gitEnsure you are in the root directory of the industrial-edge git repository by running the following command:
$ cd /path/to/your/repositoryOn your laptop or bastion host login to your cluster by exporting the
KUBECONFIGfile.$ export KUBECONFIG=~/my-ocp-cluster/auth/kubeconfigDeploy the industrial edge pattern:
./pattern.sh make install
The make install target deploys the Validated Patterns Operator, all the resources that are defined in the values-datacenter.yaml
Validating the Environment
Verify that the following Operators are installed on the HUB cluster:
$ oc get operators.operators.coreos.com -A NAME AGE advanced-cluster-management.open-cluster-management 10m amq-broker-rhel8.manuela-tst-all 10m amq-streams.manuela-data-lake 10m amq-streams.manuela-tst-all 10m camel-k.manuela-data-lake 10m camel-k.manuela-tst-all 10m cephcsi-operator.openshift-storage 10m mcg-operator.openshift-storage 10m multicluster-engine.multicluster-engine 7m19s ocs-client-operator.openshift-storage 10m ocs-operator.openshift-storage 10m odf-csi-addons-operator.openshift-storage 10m odf-operator.openshift-storage 10m odf-prometheus-operator.openshift-storage 10m openshift-gitops-operator.openshift-operators 17m openshift-pipelines-operator-rh.openshift-operators 10m patterns-operator.openshift-operators 17m recipe.openshift-storage 10m rhods-operator.redhat-ods-operator 10m rook-ceph-operator.openshift-storage 10mNote: The list above was taken on OpenShift 4.17. It might change slightly depending on the OpenShift version being used. For example, odf has fewer operator components on OpenShift 4.15 and earlier.
Access the ArgoCD environment
You can find the ArgoCD application links listed under the nine box Red Hat applications in the OpenShift Container Platform web console.
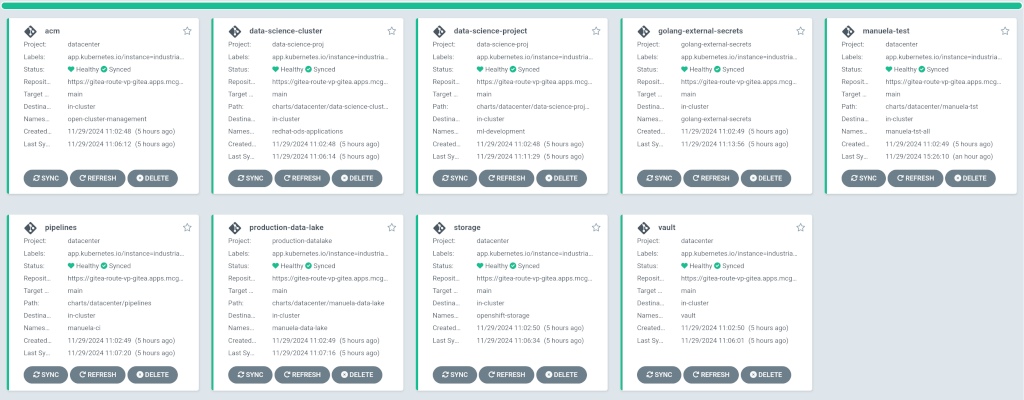
The most important ArgoCD instance to examine at this point is the
Datacenter ArgoCD. This is where all the applications for the datacenter, including the test environment, can be tracked.Check that all applications are synchronised. It should look like the following:
Uninstalling
We currently do not support uninstalling this pattern.
