This pattern is based on the OpenShift AI tutorial for fraud detection.
MLOps Fraud Detection

About the MLOps Fraud Detection Pattern
| This pattern has been reworked for a modern RHOAI experience. To see the original pattern, check out the legacy branch. |
- MLOps Credit Card Fraud Detection use case
Build, train and serve models in RHOAI to detect credit card fraud
Use Kubeflow pipelines in RHOAI for declarative model building workflows
Store models in S3-compatible storage with Minio
Serve ML models using Kserve on RHOAI
- Background
AI technology is already transforming the financial services industry. AI models can be used to make rapid inferences that benefit the FS institute and its customers. This pattern deploys a AI model to detect fraud on crdit card transactions
About the solution
The model is built on a Credit Card Fraud Detection model, which predicts if a credit card usage is fraudulent or not depending on a few parameters such as: distance from home and last transaction, purchase price compared to median, if it’s from a retailer that already has been purchased from before, if the PIN number is used and if it’s an online order or not.
Technology Highlights:
Event-Driven Architecture
Data Science on Red Hat OpenShift AI
Declarative MLOps pipeline with Kubeflow
ML model serving with Kserve
Solution Discussion
This architecture pattern demonstrates four strengths:
Real-Time Processing: Analyze transactions in real-time, quickly identifying and flagging potentially fraudulent activities. This speed is crucial in preventing unauthorized transactions before they are completed.
Pattern Recognition: Detect patterns and anomalies in data and learn from historical transaction data to identify typical spending patterns of a cardholder and flag transactions that deviate from these patterns.
Cost Efficiency: By automating the detection process, AI reduces the need for extensive manual review of transactions, which can be time-consuming and costly.
Flexibility and Agility: An cloud native architecture that supports the use of microservices, containers, and serverless computing, allowing for more flexible and agile development and deployment of AI models. This means faster iteration and deployment of new fraud detection algorithms.
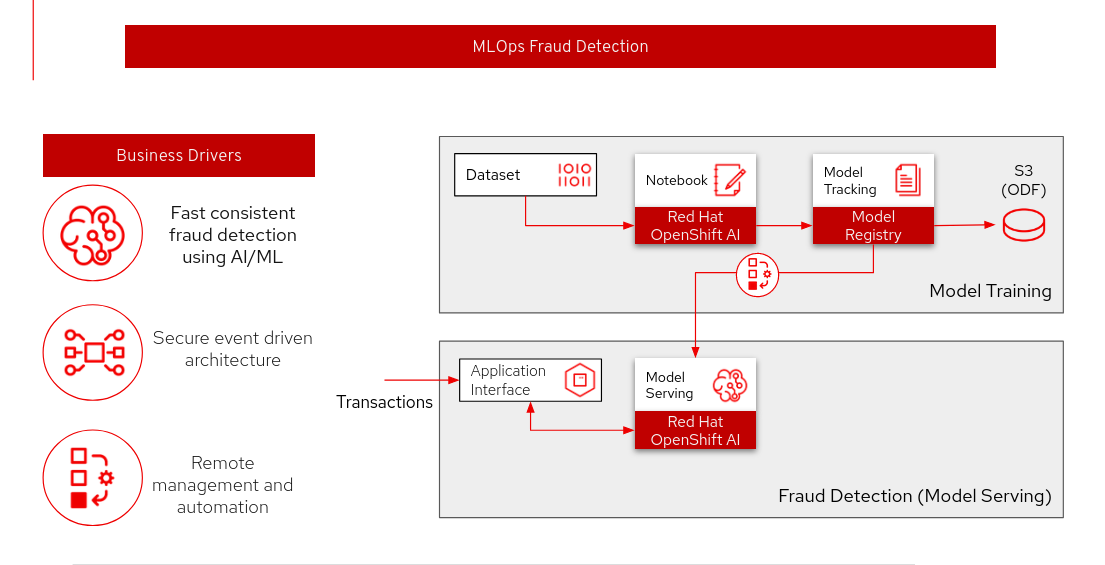
Overview of the Architecture
Description of each component:
Data Set: The dataset contains the data used for training and evaluating the model built in this tutorial. The dataset is sourced from the github.com/rh-aiservices-bu/fraud-detection
Kubeflow Pipeline: The Kubeflow pipeline builds, trains, and uploads the model. The source for this pipeline is in the pattern repository at src/kubeflow-pipelines/small-model/train_upload_model.yaml. Upon pattern installation, the system automatically runs this pipeline once to train the initial model.
S3 (Minio): Minio provides storage for the models and serves as the storage interface for the Kubeflow pipeline. While this pattern uses Minio for parity with the source tutorial, any S3-compatible storage solution is compatible.
Kserve Model Serving: The pattern uses the Kserve model serving capabilities in Red Hat OpenShift AI (RHOAI) to serve models with an OpenVINO model server.
Application interface: This interface runs predictions with the model. This pattern includes a visual interface (interactive application) built with Gradio that loads the model from Minio.
About the technology
The following technologies are used in this solution:
- Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform
An enterprise-ready Kubernetes container platform built for an open hybrid cloud strategy. It provides a consistent application platform to manage hybrid cloud, public cloud, and edge deployments. It delivers a complete application platform for both traditional and cloud-native applications, allowing them to run anywhere. OpenShift has a pre-configured, pre-installed, and self-updating monitoring stack that provides monitoring for core platform components. It also enables the use of external secret management systems, for example, HashiCorp Vault in this case, to securely add secrets into the OpenShift platform.
- Red Hat OpenShift AI
Red Hat® OpenShift® AI is an AI-focused portfolio that provides tools to train, tune, serve, monitor, and manage AI/ML experiments and models on Red Hat OpenShift. Bring data scientists, developers, and IT together on a unified platform to deliver AI-enabled applications faster.
- Red Hat OpenShift GitOps
A declarative application continuous delivery tool for Kubernetes based on the ArgoCD project. Application definitions, configurations, and environments are declarative and version controlled in Git. It can automatically push the desired application state into a cluster, quickly find out if the application state is in sync with the desired state, and manage applications in multi-cluster environments.