Deploying the Multicloud GitOps pattern
Prerequisite
- An OpenShift cluster
- To create an OpenShift cluster, go to the Red Hat Hybrid Cloud console.
- Select Services -> Containers -> Create cluster.
- The cluster must have a dynamic
StorageClassto provisionPersistentVolumes. See sizing your cluster.
- Optional: A second OpenShift cluster for multicloud demonstration.
- The git binary and podman. For details see Installing Git and Installing Podman
The use of this pattern depends on having at least one running Red Hat OpenShift cluster. It is desirable to have a cluster for deploying the GitOps management hub assets and a separate cluster(s) for the managed cluster(s).
If you do not have a running Red Hat OpenShift cluster, you can start one on a public or private cloud by using Red Hat’s cloud service.
Procedure
For installation tooling dependencies, see link:https://validatedpatterns.io/learn/quickstart/[Patterns quick start].
{% include prerequisite-tools.md %}
Fork the rh-multicloud-gitops-pxe repository on GitHub. It is recommended to fork because you can update your fork as part of the GitOps and DevOps processes.
Clone the forked copy of this repository.
git clone git@github.com:your-username/multicloud-gitops-pxe.gitCreate a local copy of the secret values file that can safely include credentials.
Warning: Do not commit this file. You do not want to push personal credentials to GitHub. Note that if you do not want to customize the secrets, these steps are not needed. The framework generates a random password for the config-demo application.
cp values-secret.yaml.template ~/values-secret-multicloud-gitops-pxe.yaml vi ~/values-secret-multicloud-gitops-pxe.yamlCustomize the deployment for your cluster.
git checkout -b my-branch vi values-global.yaml git add values-global.yaml git commit values-global.yaml git push origin my-branchYou can deploy the pattern by running
./pattern.sh make installor by using the validated pattern operator.
Deploying the cluster by using the pattern.sh file
To deploy the cluster by using the pattern.sh file, complete the following steps:
Login to your cluster using oc login or exporting the
KUBECONFIG.oc loginor set
KUBECONFIGto the path to yourkubeconfigfile. For example:export KUBECONFIG=~/my-ocp-env/hub/auth/kubeconfigDeploy the pattern to your cluster.
./pattern.sh make installVerify that the Operators have been installed.
- To verify, in the *OpenShift Container Platform web console, navigate to Operators → Installed Operators page.
2.Check that the Operator is installed in the
openshift-operatorsnamespace and its status isSucceeded.
- To verify, in the *OpenShift Container Platform web console, navigate to Operators → Installed Operators page.
2.Check that the Operator is installed in the
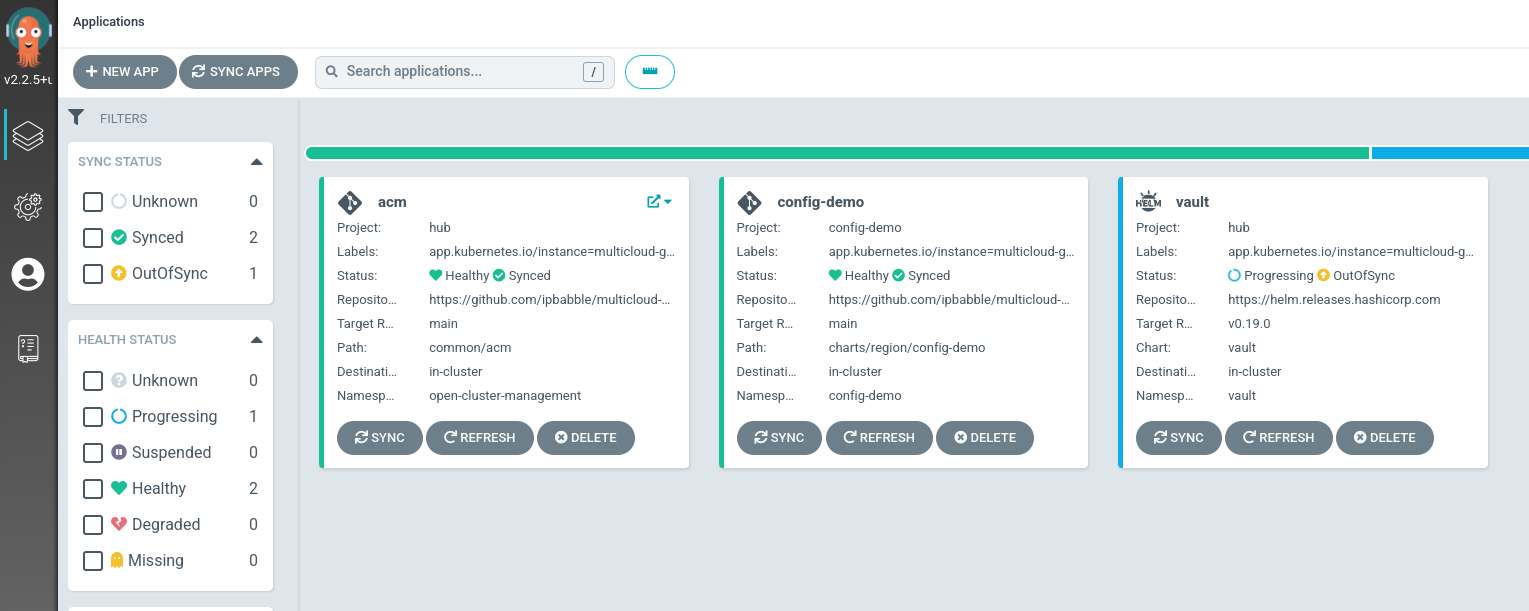
- Verify that all applications are synchronized. Under the project
multicloud-gitops-hubclick the URL for thehubgitopsserver. The Vault application is not synched.
Multicloud GitOps application demos
As part of this pattern, HashiCorp Vault has been installed. Refer to the section on Vault.
Next steps
Deploying the managed cluster applications
After the management hub is set up and works correctly, attach one or more managed clusters to the architecture (see diagrams below).
For instructions on deploying the edge, refer to Managed Cluster Sites.
Contribute to this pattern: Help & Feedback Report Bugs