Intel QAT accelerated Multicloud GitOps

Validation status:
Links:
About the Intel QAT accelerated Multicloud GitOps pattern
- Use case
Use a GitOps approach to manage hybrid and multi-cloud deployments across both public and private clouds.
Enable cross-cluster governance and application lifecycle management.
Accelerate TLS handshaking operations and improve computational performance by offloading cryptographic tasks to QAT.
Securely manage secrets across the deployment.
Simplify managing different microservices that make up a cloud-native application with Istio service mesh.
Based on the requirements of a specific implementation, certain details might differ. However, all validated patterns that are based on a portfolio architecture, generalize one or more successful deployments of a use case.
- Background
Organizations are aiming to develop, deploy, and operate applications on an open hybrid cloud in a stable, simple, and secure way. This hybrid strategy includes multi-cloud deployments where workloads might be running on multiple clusters and on multiple clouds, private or public. This strategy requires an infrastructure-as-code approach: GitOps. GitOps uses Git repositories as a single source of truth to deliver infrastructure-as-code. Submitted code checks the continuous integration (CI) process, while the continuous delivery (CD) process checks and applies requirements for things like security, infrastructure-as-code, or any other boundaries set for the application framework. All changes to code are tracked, making updates easy while also providing version control should a rollback be needed. Moreover, organizations which are looking to deliver distributed applications at scale can make these applications faster by offloading cryptographic tasks to Intel QuickAssist Technology.
About the solution
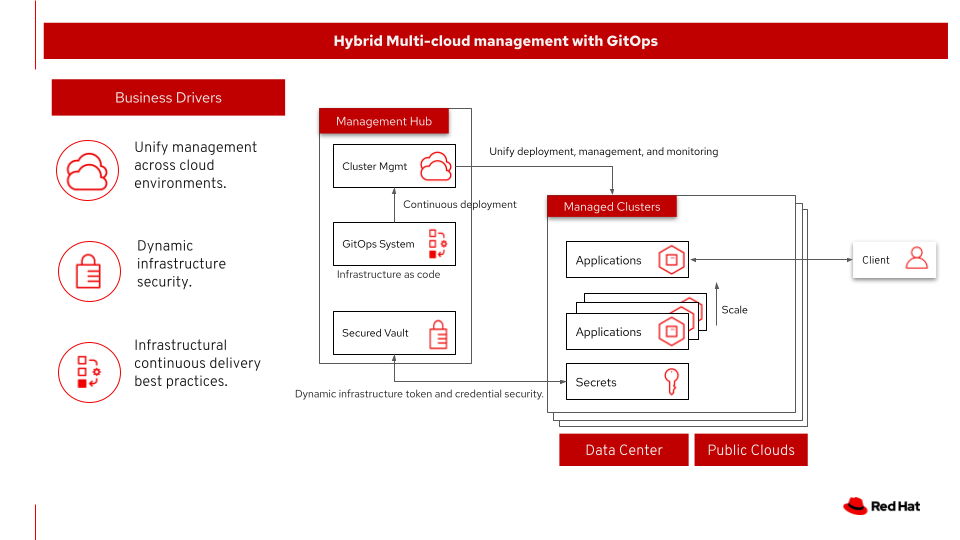
This architecture covers hybrid and multi-cloud management with GitOps as shown in following figure. At a high level this requires a management hub, for DevOps and GitOps, and infrastructure that extends to one or more managed clusters running on private or public clouds. The automated infrastructure-as-code approach can manage the versioning of components and deploy according to the infrastructure-as-code configuration.
Benefits of Hybrid Multicloud management with GitOps:
Unify management across cloud environments.
Dynamic infrastructure security.
Infrastructural continuous delivery best practices.

Figure 1. Overview of the solution including the business drivers, management hub, and the clusters under management
In the following figure, logically, this solution can be viewed as being composed of an automation component, unified management including secrets management, and the clusters under management, all running on top of a user-chosen mixture of on-premise data centers and public clouds.
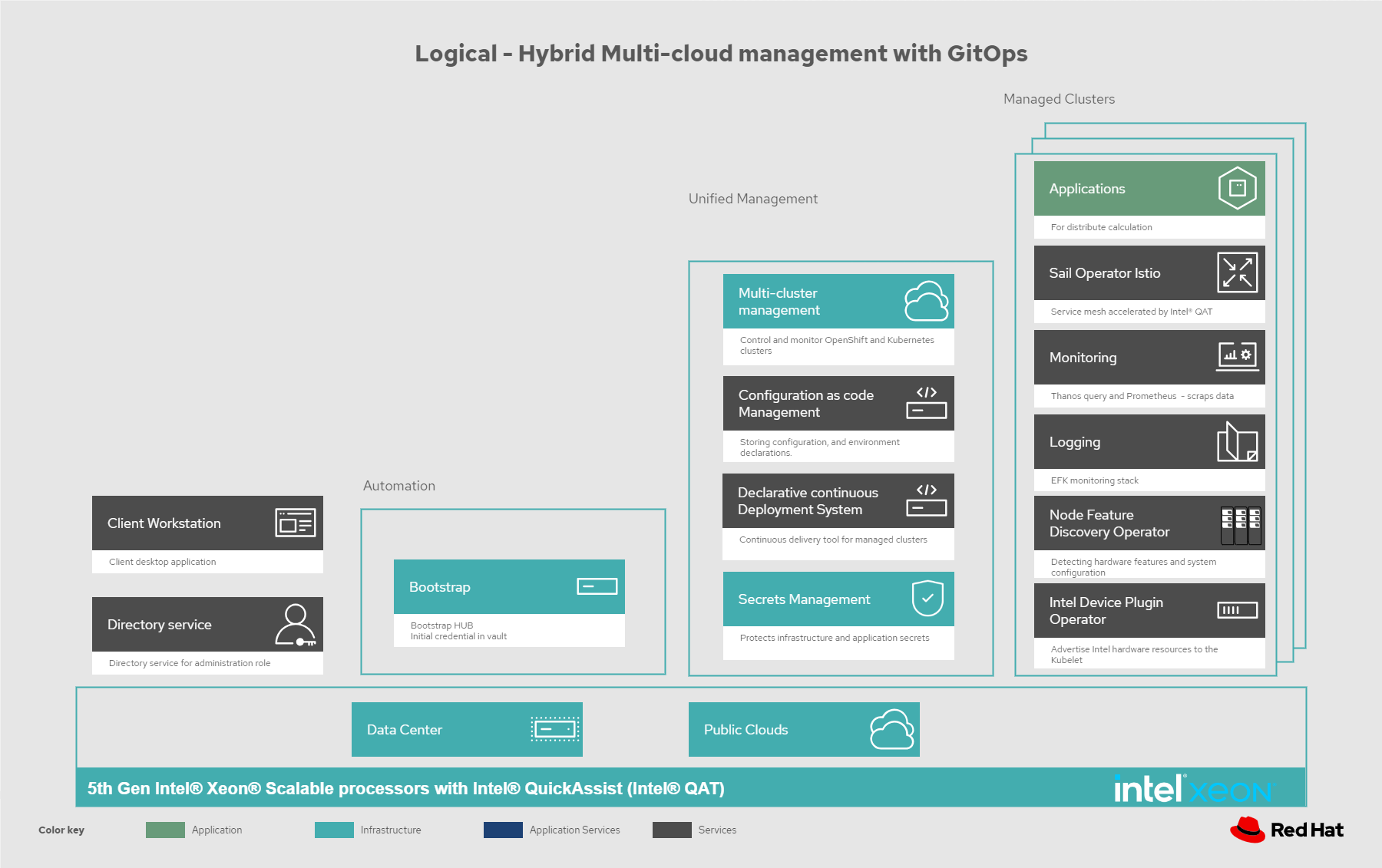
Figure 2. Logical diagram of Intel QAT accelerated hybrid multi-cloud management with GitOps
About the technology
The following technologies are used in this solution:
- Red Hat OpenShift Platform
An enterprise-ready Kubernetes container platform built for an open hybrid cloud strategy. It provides a consistent application platform to manage hybrid cloud, public cloud, and edge deployments. It delivers a complete application platform for both traditional and cloud-native applications, allowing them to run anywhere. OpenShift has a pre-configured, pre-installed, and self-updating monitoring stack that provides monitoring for core platform components. It also enables the use of external secret management systems, for example, HashiCorp Vault in this case, to securely add secrets into the OpenShift platform.
- Red Hat OpenShift GitOps
A declarative application continuous delivery tool for Kubernetes based on the ArgoCD project. Application definitions, configurations, and environments are declarative and version controlled in Git. It can automatically push the desired application state into a cluster, quickly find out if the application state is in sync with the desired state, and manage applications in multi-cluster environments.
- Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes
Controls clusters and applications from a single console, with built-in security policies. Extends the value of Red Hat OpenShift by deploying apps, managing multiple clusters, and enforcing policies across multiple clusters at scale.
- Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform
Provides an enterprise framework for building and operating IT automation at scale across hybrid clouds including edge deployments. It enables users across an organization to create, share, and manage automation, from development and operations to security and network teams.
- Node Feature Discovery Operator
Manages the detection of hardware features and configuration in an OpenShift Container Platform cluster by labeling the nodes with hardware-specific information. NFD labels the host with node-specific attributes, such as PCI cards, kernel, operating system version, and so on.
- Intel® QuickAssist Technology
Accelerate data encryption and compression for applications from networking to enterprise, cloud to storage, and content delivery to database with Intel® QuickAssist Technology.
- Intel® Device Plugin Operator
The Intel Technology Enabling for OpenShift project provides Intel Data Center hardware feature-provisioning technologies with the Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform (RHOCP).
- Sail Operator, Istio Operator for Red Hat OpenShift
A service mesh is a dedicated infrastructure layer that you can add to your applications. It allows you to transparently add capabilities like observability, traffic management, and security, without adding them to your code. Sail Operator serves as the foundation for Red Hat OpenShift Service Mesh 3.
- Hashicorp Vault
Provides a secure centralized store for dynamic infrastructure and applications across clusters, including over low-trust networks between clouds and data centers.
This solution also uses a variety of observability tools including the Prometheus monitoring and Grafana dashboard that are integrated with OpenShift as well as components of the Observatorium meta-project which includes Thanos and the Loki API.
Overview of the architectures
The following figure provides a schematic diagram overview of the complete solution including both components and data flows.
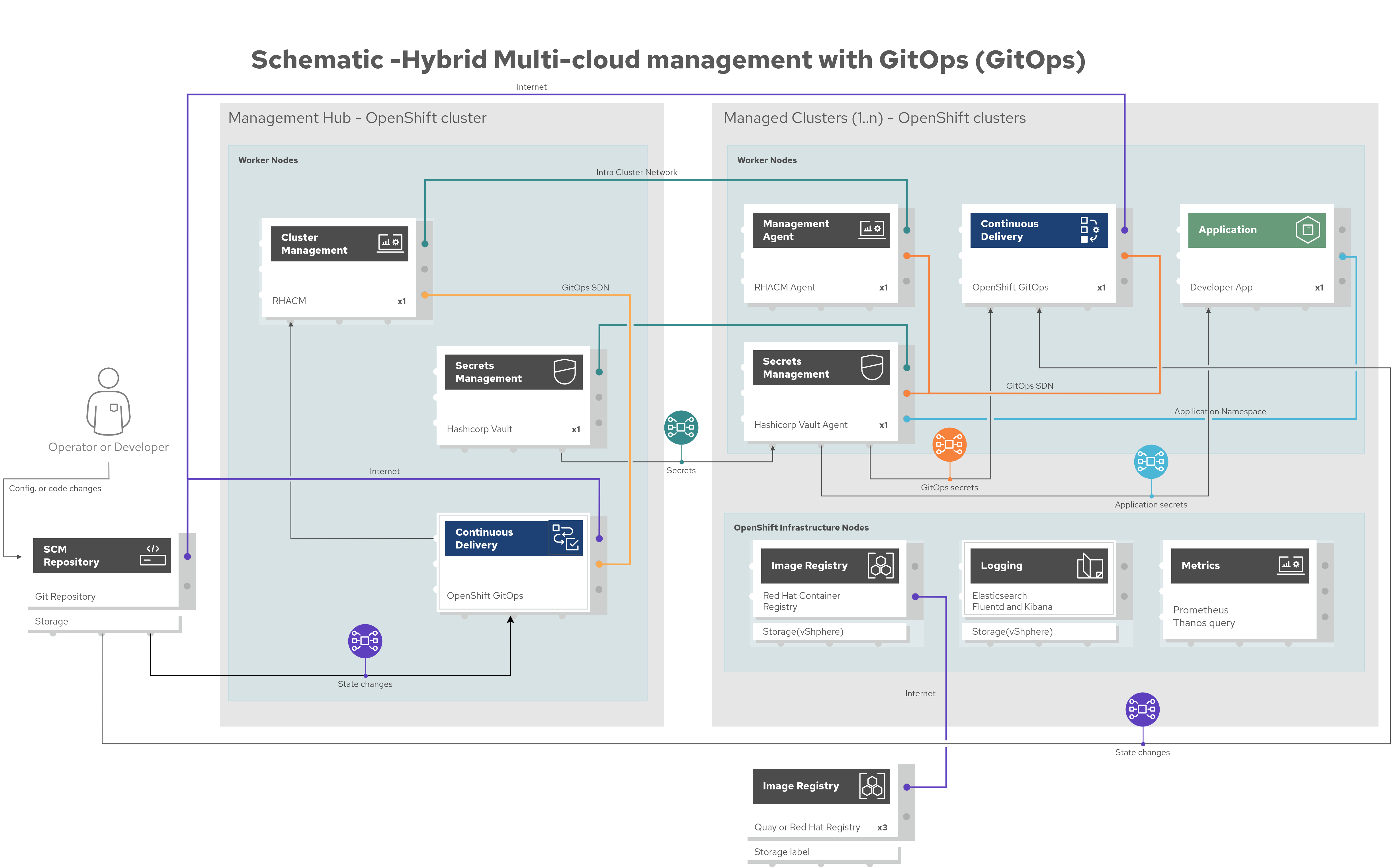
Figure 3. Overview schematic diagram of the complete solution
Subsequent schematic diagrams provide details on:
Bootstrapping the management hub (Figure 4)
Hybrid multi-cloud GitOps (Figure 5)
Dynamic security management (Figure 6)
Bootstrapping the management hub
The following figure provides a schematic diagram showing the setup of the management hub using Ansible playbooks.
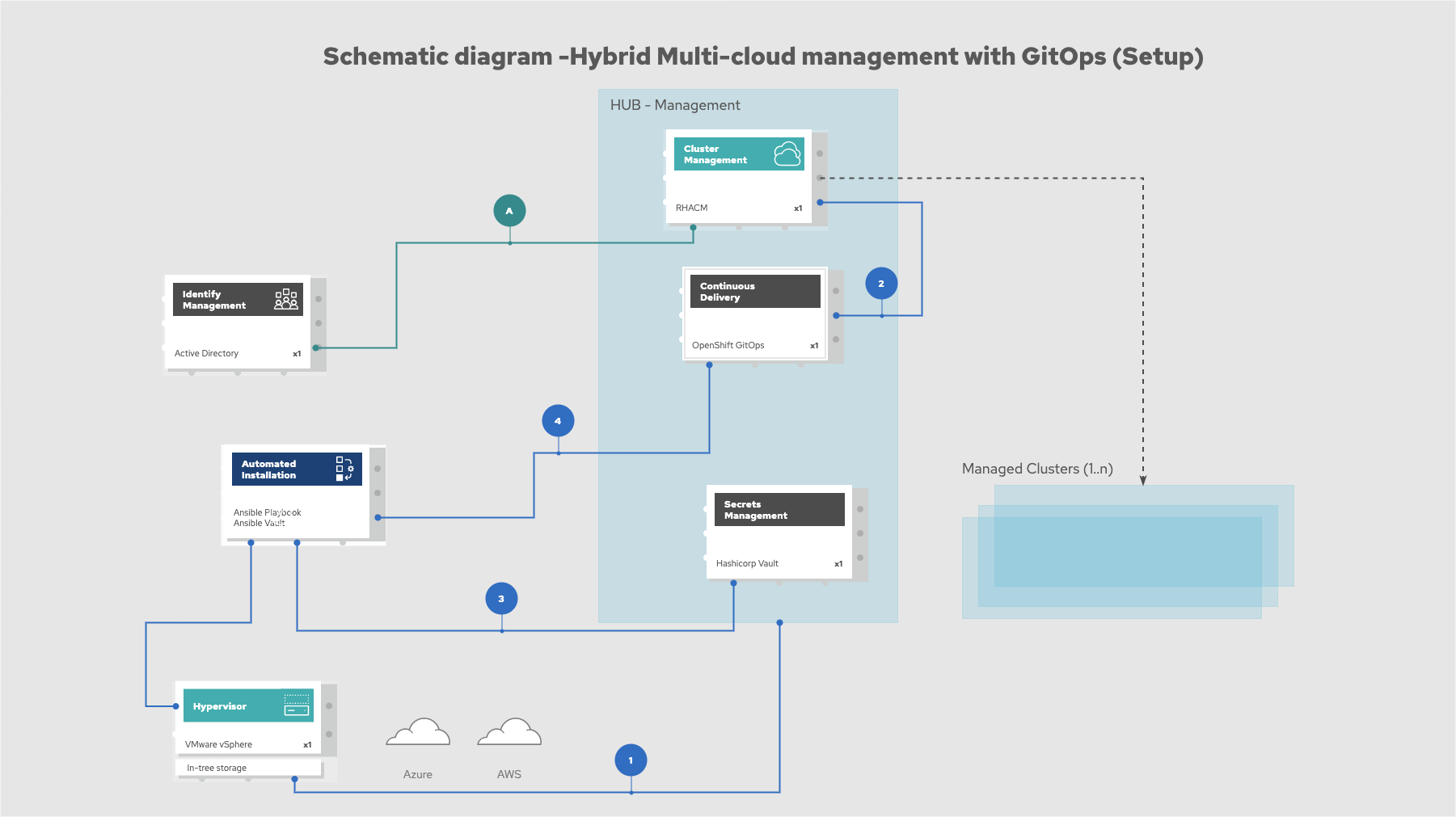
Figure 4. Schematic diagram of bootstrapping the management hub
Set up the OpenShift Container Platform that hosts the Management Hub. The OpenShift installation program provides flexible ways to install OpenShift. An Ansible playbook starts the installation with necessary configurations.
Ansible playbooks deploy and configure Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes and, later, other supporting components such as external secrets management, on top of the provisioned OpenShift cluster.
Another Ansible playbook installs HashiCorp Vault, a Red Hat partner product chosen for this solution that can be used to manage secrets for OpenShift clusters.
An Ansible playbook configures and installs the Openshift GitOps operator on the hub cluster. This deploys the Openshift GitOps instance to enable continuous delivery.
Hybrid Multicloud GitOps
The following figure provides a schematic diagram showing remaining activities associated with setting up the management hub and clusters using Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management.
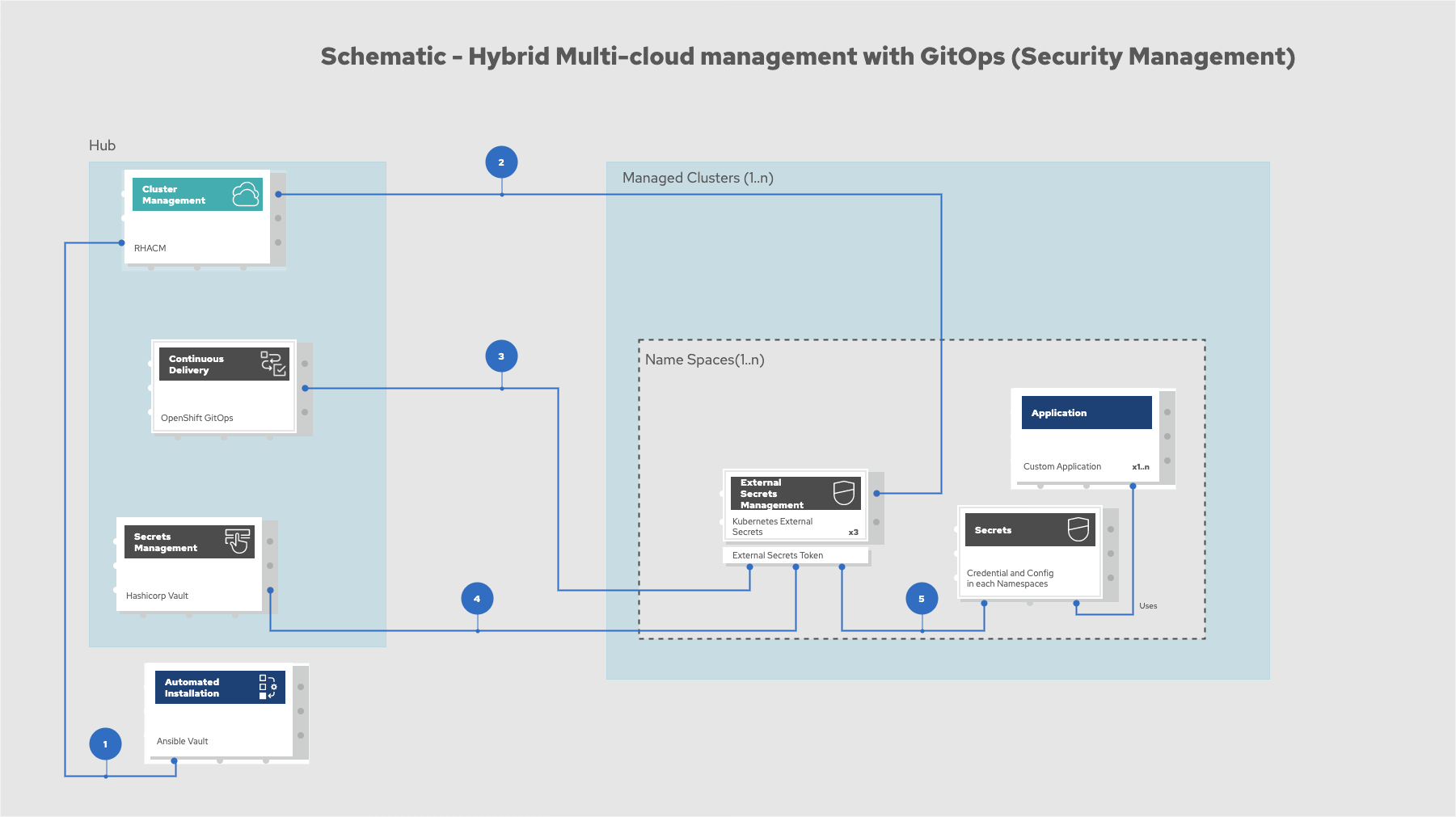
Figure 5. Schematic diagram of hybrid multi-cloud management with GitOps
Manifest and configuration are set as code template in the form of a
KustomizationYAML file. The file describes the desired end state of the managed cluster. When complete, theKustomizationYAML file is pushed into the source control management repository with a version assigned to each update.OpenShift GitOps monitors the repository and detects changes in the repository.
OpenShift GitOps creates and updates the manifest by creating Kubernetes objects on top of Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management.
Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management provisions, updates, or deletes managed clusters and configuration according to the manifest. In the manifest, you can configure what cloud provider the cluster will be on, the name of the cluster, infrastructure node details and worker node. Governance policy can also be applied as well as provision an agent in the cluster as the bridge between the control center and the managed cluster.
OpenShift GitOps continuously monitors the code repository and the status of the clusters reported back to Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management. Any configuration drift or in case of any failure, OpenShift GitOps will automatically try to remediate by applying the manifest or by displaying alerts for manual intervention.
Dynamic security management
The following figure provides a schematic diagram showing how secrets are handled in this solution.

Figure 6. Schematic showing the setup and use of external secrets management
During setup, the token to securely access HashiCorp Vault is stored in Ansible Vault. It is encrypted to protect sensitive content.
Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes acquires the token from Ansible Vault during install and distributes it among the clusters. As a result, you have centralized control over the managed clusters through RHACM.
To allow the cluster access to the external vault, you must set up the external secret management with Helm in this study. OpenShift Gitops is used to deploy the external secret object to a managed cluster.
External secret management fetches secrets from HashiCorp Vault by using the token that was generated in step 2 and constantly monitors for updates.
Secrets are created in each namespace, where applications can use them.
Additional resources
View and download all of the diagrams above from the Red Hat Portfolio Architecture open source tooling site.
Intel QAT accelerated Multicloud GitOps pattern
The basic Multicloud GitOps pattern has been extended to highlight the 5th Generation Intel Xeon Scalable Processors capabilities, offering developers a streamlined pathway to accelerate their workloads through the integration of Intel QAT.
The basic pattern has been extended by 4 components: Intel Device Plugin Operator, Node Feature Discovery Operator (NFD), Sail Operator, and simple HTTP request and response application. The main purpose of this extension is to enable TLS handshaking and showcase how Intel QAT accelerates cryptographic operations.
Intel Device Plugin Operator’s task is to expose QAT resources to the Openshift layer, so it makes it easy to use when creating deployments. After QAT resources are properly exposed Node Feature Discovery Operator is deployed. NFD manages the detection of hardware features and configuration in an OpenShift Container Platform cluster. It labels the nodes with hardware-specific information.
Sail Operator deploys Istio Service Mesh. It is basically an extra layer added on top of user applications, and it adds capabilities like traffic management between services and security, without manually adding them to code. The Istio version deployed by Sail Operator allows for additional configuration, that is enabling Intel QAT in cryptographic operations. The last added component is the httpbin application, which is HTTP request and response service used for testing and showcase purposes. The workload idea was based on Istio’s official instructions on how to setup secure TLS ingress gateway.
The appearance of qat as a private key provider in Istio ingress gateway pod logs confirms that Intel QAT is used:
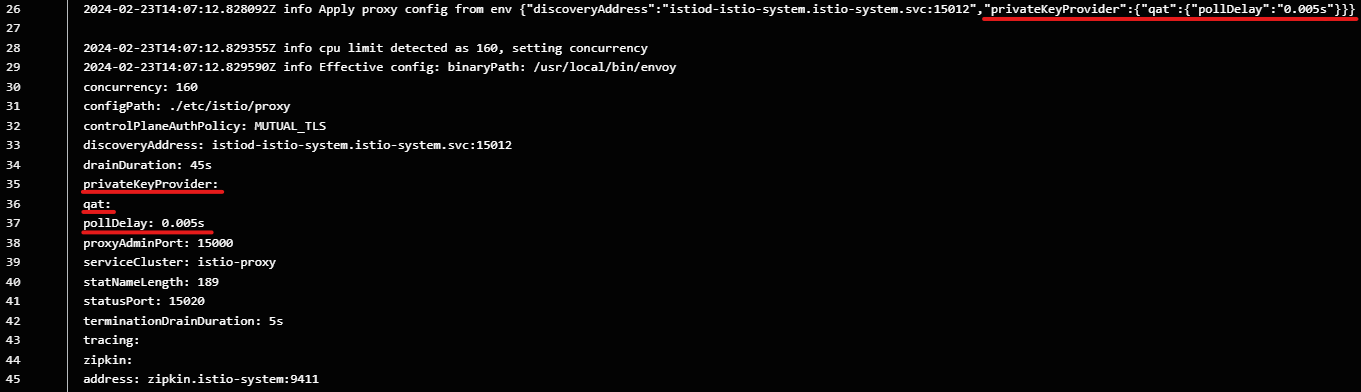
Figure 7. Logs from Istio ingress gateway pod
Next steps
Deploy the management hub using Helm.
Add a managed cluster to deploy the managed cluster piece using ACM.
