RAG LLM Chatbot on CPU
Validation status:
Links:
CPU-based RAG LLM chatbot
Introduction
The CPU-based RAG LLM chatbot Validated Pattern deploys a retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) chatbot on Red Hat OpenShift by using Red Hat OpenShift AI. The pattern runs entirely on CPU nodes without requiring GPU hardware, which provides a cost-effective and accessible solution for environments where GPU resources are limited or unavailable. This pattern provides a secure, flexible, and production-ready starting point for building and deploying on-premise generative AI applications.
Target audience
This pattern is intended for the following users:
- Developers & Data Scientists who want to build and experiment with RAG-based large language model (LLM) applications.
- MLOps & DevOps Engineers who are responsible for deploying and managing AI/ML workloads on OpenShift.
- Architects who evaluate cost-effective methods for delivering generative AI capabilities on-premise.
Why Use This Pattern?
- Cost-Effective: The pattern runs entirely on CPU nodes, which removes the need for expensive and scarce GPU resources.
- Flexible: The pattern supports multiple vector database backends, such as Elasticsearch, PGVector, and Microsoft SQL Server, to integrate with existing data infrastructure.
- Transparent: The Gradio frontend exposes the internals of the RAG query and LLM prompts, which provides insight into the generation process.
- Extensible: The pattern uses open-source standards, such as KServe and OpenAI-compatible APIs, to serve as a foundation for complex applications.
Architecture Overview
At a high level, the components work together in the following sequence:
- A user enters a query into the Gradio UI.
- The backend application, using LangChain, queries a configured vector database to retrieve relevant documents.
- These documents are combined with the original query from the user into a prompt.
- The prompt is sent to the KServe-deployed LLM, which runs via llama.cpp on a CPU node.
- The LLM generates a response, which is streamed back to the Gradio UI.
- Vault provides the necessary credentials for the vector database and HuggingFace token at runtime.
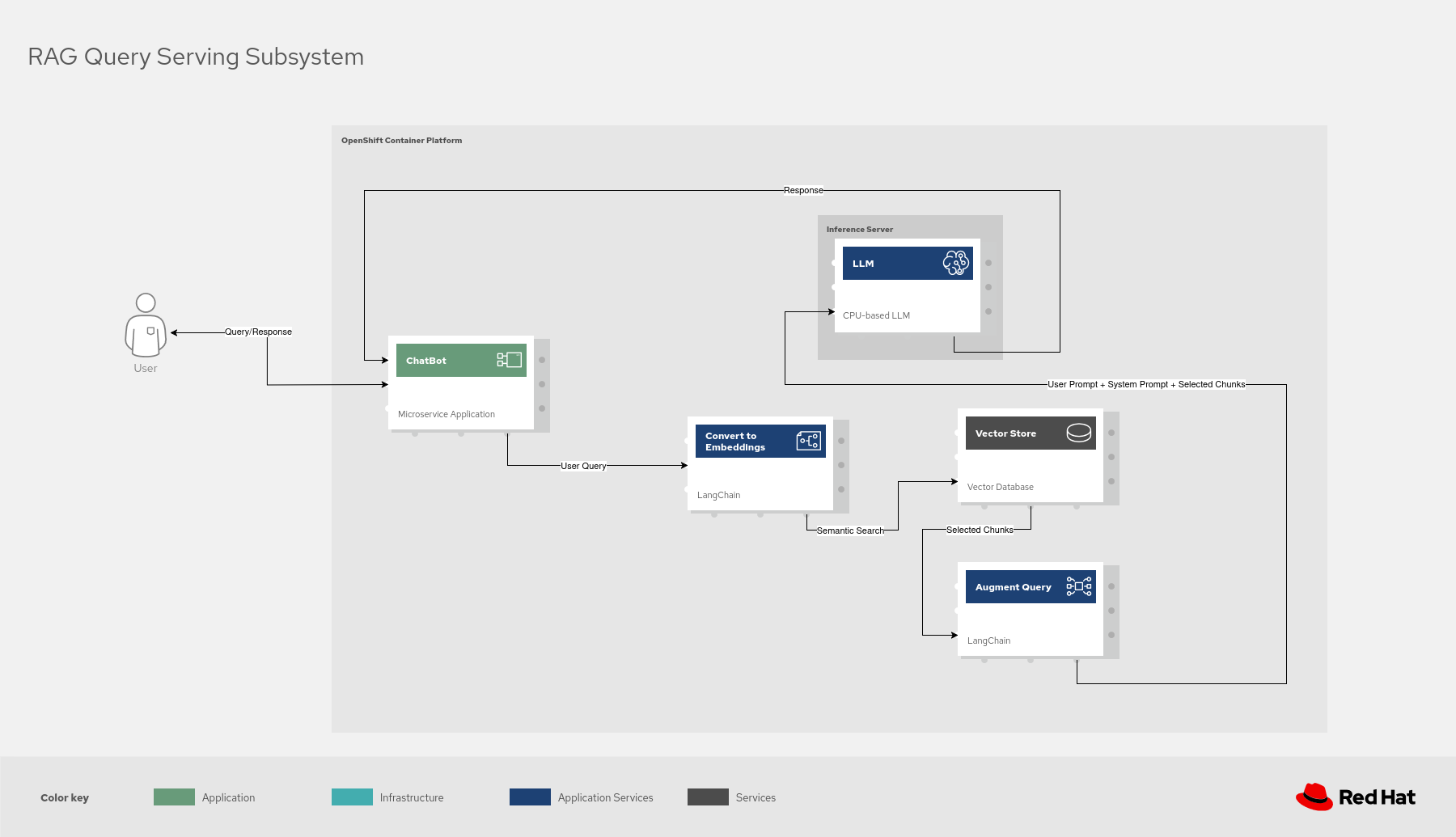
Figure 1. Overview of RAG Query from User’s perspective.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, ensure that you have access to the following resources:
- A Red Hat OpenShift cluster version 4.x. (The recommended size is at least two
m5.4xlargenodes.) - A HuggingFace API token.
- The
Podmancommand-line tool.
What This Pattern Provides
- A KServe-based LLM deployed to Red Hat OpenShift AI that runs entirely on a CPU-node with a llama.cpp runtime.
- A choice of one or more vector database providers to serve as a RAG backend with configurable web-based or Git repository-based sources. Vector embedding and document retrieval are implemented with LangChain.
- Vault-based secret management for a HuggingFace API token and credentials for supported databases, such as (Elasticsearch, PGVector, Microsoft SQL Server).
- A gradio-based frontend for connecting to multiple OpenAI API-compatible LLMs. This frontend exposes the internals of the RAG query and LLM prompts so that users have insight into the running processes.
