AI Generation with LLM and RAG
Document generation demo with LLM and RAG
Introduction
This deployment is based on the Validated Patterns framework, using GitOps for seamless provisioning of all operators and applications. It deploys a Chatbot application that harnesses the power of Large Language Models (LLMs) combined with the Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) framework.
The pattern uses the Red Hat OpenShift AI to deploy and serve LLM models at scale.
The pattern provides several options for the RAG DB vector store including EDB Postgres (the default), Elasticsearch, Redis, and Microsoft SQL Server.
Demo Description & Architecture
The goal of this demo is to showcase a Chatbot LLM application augmented with data from Red Hat product documentation running on Red Hat OpenShift AI. It deploys an LLM application that connects to multiple LLM providers such as OpenAI, Hugging Face, and NVIDIA NIM. The application generates a project proposal for a Red Hat product.
Key Features
- Leveraging Red Hat OpenShift AI to deploy and serve LLM models powered by NVIDIA GPU accelerator.
- LLM Application augmented with content from Red Hat product documentation.
- Multiple LLM providers (OpenAI, Hugging Face, NVIDIA).
- Vector Database, such as EDB Postgres, Elasticsearch, or Microsoft SQL Server to store embeddings of Red Hat product documentation.
- Monitoring dashboard to provide key metrics such as ratings.
- GitOps setup to deploy e2e demo (frontend / vector database / served models).
RAG Demo Workflow

Figure 3. Schematic diagram for workflow of RAG demo with Red Hat OpenShift.
RAG Data Ingestion

Figure 4. Schematic diagram for Ingestion of data for RAG.
RAG Augmented Query
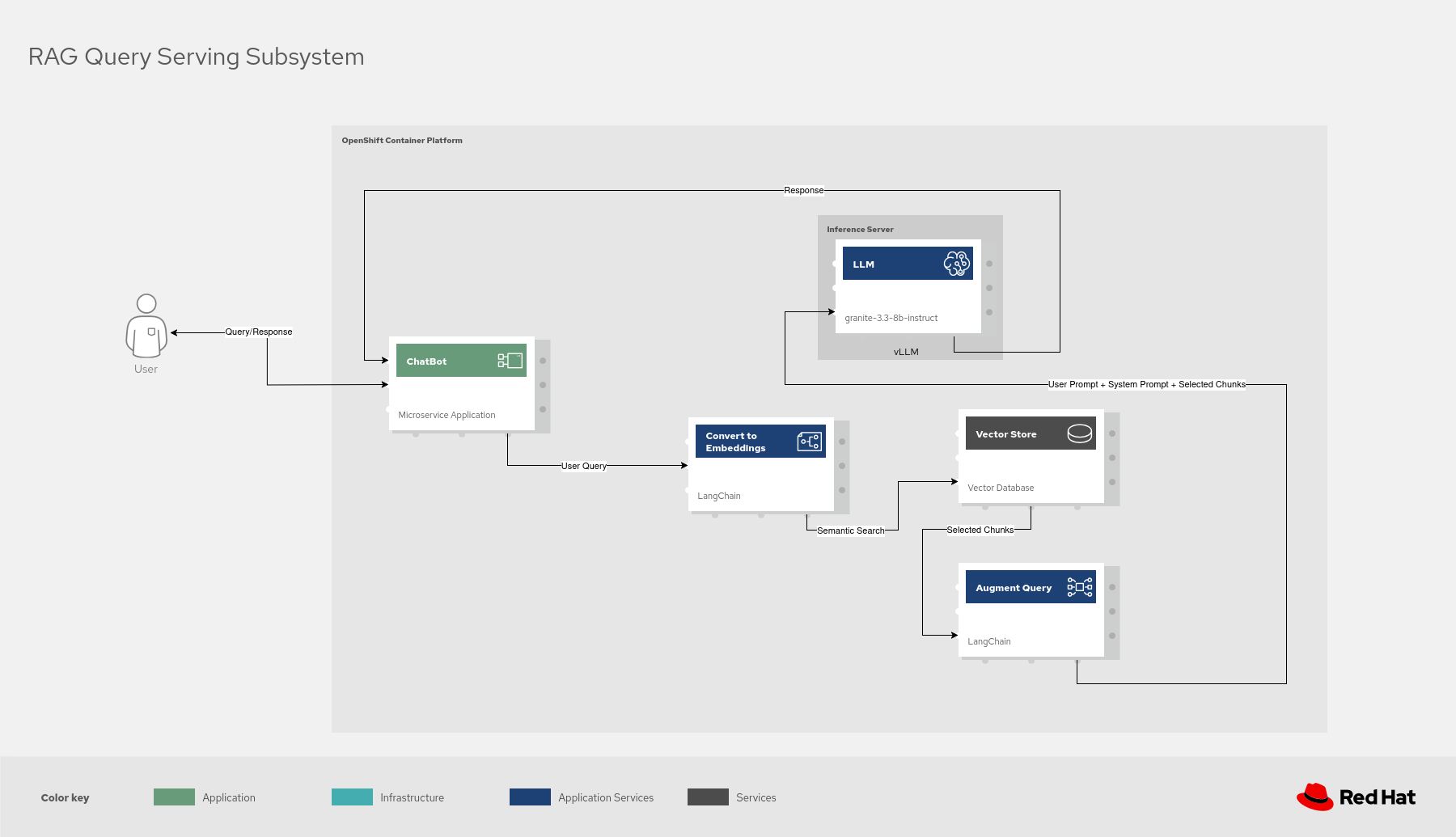
Figure 5. Schematic diagram for RAG demo augmented query.
In Figure 5, we can see RAG augmented query. The granite-3.3-8b-instruct model is used for
language processing. LangChain is used to integrate different tools of the LLM-based
application together and to process the PDF files and web pages. A vector
database provider such as EDB Postgres for Kubernetes (or Elasticsearch), is used to
store vectors. vLLM is used to serve the granite-3.3-8b-instruct model. Gradio is
used for user interface and object storage to store language model and other
datasets. Solution components are deployed as microservices in the Red Hat
OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
Download diagrams
View and download all of the diagrams above in our open source tooling site.
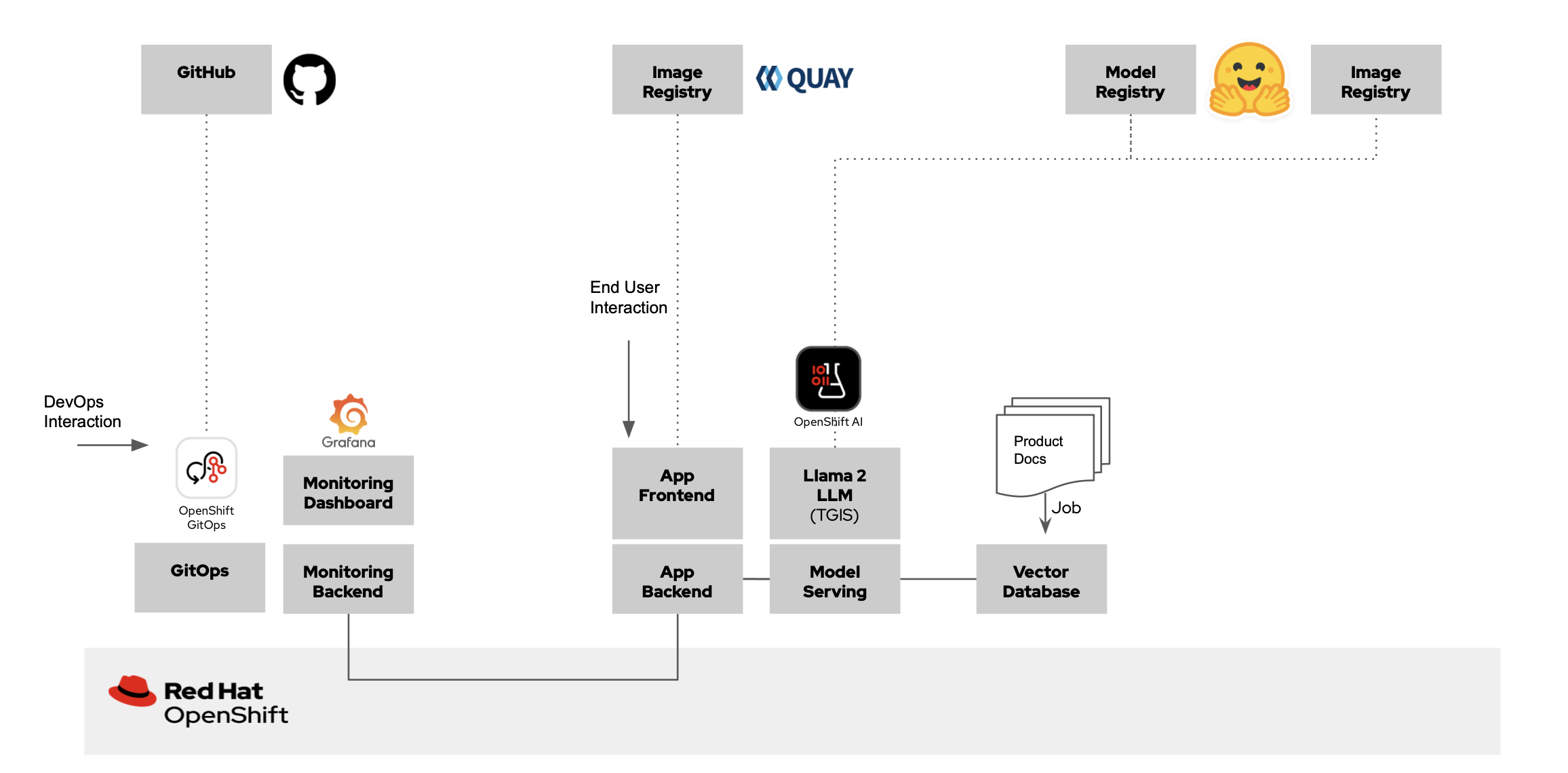
Figure 6. Proposed demo architecture with OpenShift AI
Components deployed
- vLLM Inference Server: The pattern deploys a vLLM server. The server deploys
ibm-granite/granite-3.3-8b-instructmodel. The server will require a GPU node. - EDB Postgres for Kubernetes / Redis Server: A Vector Database server is deployed to store vector embeddings created from Red Hat product documentation.
- Populate VectorDb Job: The job creates the embeddings and populates the vector database.
- LLM Application: This is a Chatbot application that can generate a project proposal by augmenting the LLM with the Red Hat product documentation stored in vector db.
- Prometheus: Deploys a prometheus instance to store the various metrics from the LLM application and vLLM inference server.
- Grafana: Deploys Grafana application to visualize the metrics.

Figure 1. Overview of the validated pattern for RAG Demo with Red Hat OpenShift

Figure 2. Logical diagram of the RAG Demo with Red Hat OpenShift.
