Regional Disaster Recovery

OpenShift Regional Disaster Recovery
About OpenShift Regional Disaster Recovery
As more and more institution and mission critical organizations are moving in the cloud, the possible impact of having a provider failure, might this be only related to only one region, is very high.
This pattern is designed to prove the resiliency capabilities of Red Hat OpenShift in such scenario.
The Regional Disaster Recovery Pattern is designed to set up multiple instances of OpenShift Container Platform cluster connected between them to prove multi-region resiliency by maintaining the application running in the event of a regional failure.
In this scenario we will be working in a Regional Disaster Recovery setup, and the synchronization parameters can be specified in the value file.
NOTE: please consider using longer times if you have a large dataset or very long distances between the clusters
Background
The Regional DR Validated Pattern for Red Hat OpenShift increases the resiliency of your applications by connecting multiple clusters across different regions. This pattern uses Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management to offer a Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation-based multi-region disaster recovery plan if an entire region fails.
Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation offers two solutions for disaster recovery: Metro DR and Regional DR. As their name suggests, Metro DR refers to a metropolitan area disasters, which occur when the disaster covers only a single area in a region (availability zone), and Regional DR refers to when the entire region fails. Currently, only active-passive mode is supported.
A word on synchronization. A metropolitan network generally offers less latency; data can be written to multiple targets simultaneously, a feature required for active-active DR designs. On the other hand, writing to multiple targets in a cross-regional network might introduce unbearable latency to data synchronization and our applications. Therefore, Regional DR can only work with active-passive DR designs, where the targets are replicated asynchronously.
The synchronization between Availability Zones is faster and can be performed synchronous. However, in order don’t include a lot of latency on the data synchronization process, when data is replicated across regions, it necessary includes latencies based on the distance between both regions (e.g. The latency between two regions on Europe, will always be less than between Europe and Asia, so consider this when designing your infrastructure deployment on the values files of the pattern). This is the main reason because this RegionalDR is configured in an Active-Passive mode.
It requires an already existing OpenShift cluster, which will be used for installing the pattern, deploying active and passive clusters manage the application scheduling.
Prerequisites
Installing this pattern requires:
- One online Red Hat OpenShift cluster to become the “Manager” cluster. This cluster will orchestrate application deployments and data synchronizations.
- Connection to a Cloud Provider (AWS/Azure/GCP) configured in the Manager cluster. This is required for deploying the active and passive OCP clusters.
- Red Hat OpenShift CLI installed
Solution elements
The Regional DR Pattern leverages Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation’s Regional DR solution, automating applications failover between Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management managed clusters in different regions.
- The pattern is kick-started by ansible and uses ACM to overlook and orchestrate the process
- The demo application uses MongoDB writing its data on a Persistent Volume Claim backed by ODF
- We have developed a DR trigger which will be used to start the DR process
- The end user needs to configure which PV’s need synchronization and the latencies
- ACS Can be used for eventual policies
- The clusters are connected by submariner and, to have a faster recovery time, we suggest having hybernated clusters ready to be used
Red Hat Technologies
- Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform
- Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation
- Red Hat OpenShift GitOps
- Red Hat OpenShift Advanced Cluster Management
- Red Hat OpenShift Advanced Cluster Security
Operators and Technologies this Pattern Uses
Tested on
- Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform v4.13
- Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform v4.14
- Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform v4.15
Architecture
This section explains the architecture deployed by this Pattern and its Logical
and Physical perspectives.
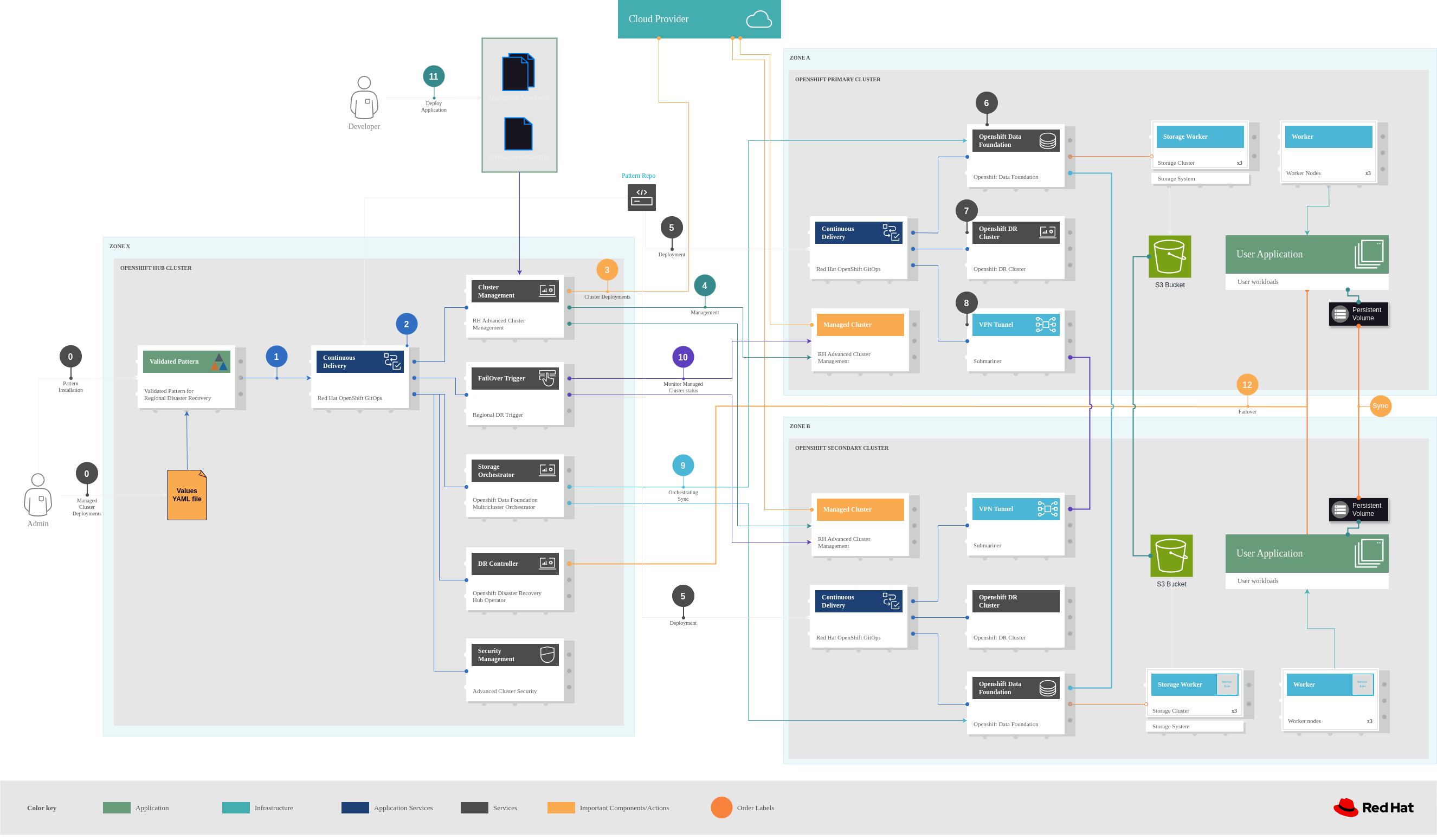
Logical architecture

Installation
This pattern is designed to be installed in an OpenShift cluster which will work as the orchestrator for the other clusters involved. The Adanced Cluster Manager installed will neither run the applications nor store any data from them, but it will take care of the plumbing of the various clusters involved, coordinating their communication and orchestrating when and where an application is going to be deployed.
As part of the pattern configuration, the administrator needs to define both clusters installation details as would be done using the Openshift-installer binary.
For installing the pattern, follow the next steps:
- Fork the Pattern.
- Describe the instructions for creating the clusters and syncing data between them.
- Commit and push your changes (to your fork).
- Set your secret cloud provider credentials.
- Connect to your target Hub cluster.
- Install the Pattern.
- Start deploying resilient applications.
Pattern Configuration
For a full example, check the Pattern’s values.yaml. The install-config specifications are detailed here.
Detailed configuration instructions can be found here.
Owners
For any request, bug report or comment about this pattern, please forward it to:
- Alejandro Villegas (avillega@rehat.com)
- Tomer Figenblat (tfigenbl@redhat.com)
